Jan 6, 2023
6G wireless technology could use humans as a power source, study explains
Posted by Liliana Alfair in categories: biotech/medical, internet, wearables
What percentage of your battery is used…
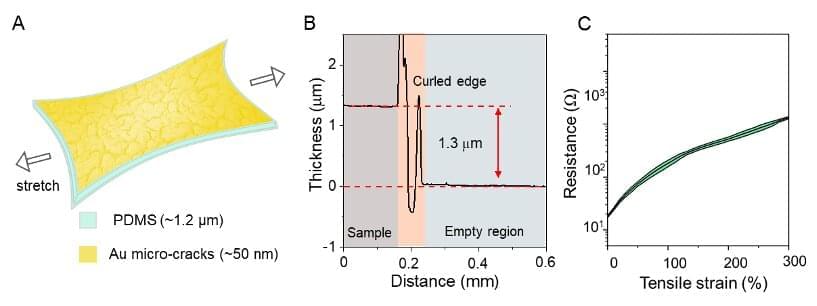
AMHERST, Mass. – 5G wireless technology is just starting to take off worldwide, but a new study is already speculating on the future of 6G! Researchers from the University of Massachusetts-Amherst say, unlike older technology, 6G could end up using people as antennas.
Continue reading “6G wireless technology could use humans as a power source, study explains” »