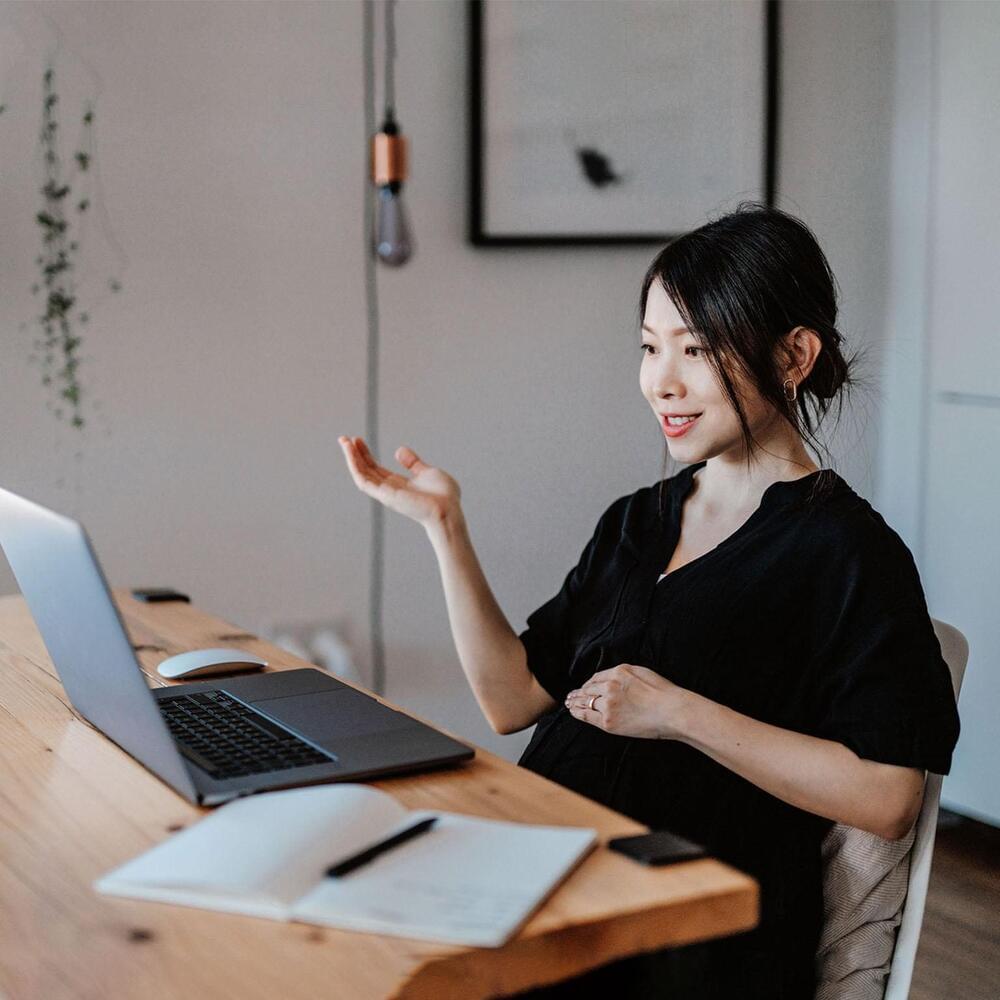
The results of the American Opportunity Survey reflect sweeping changes in the US workforce, including the equivalent of 92 million workers offered flexible work, 80 million workers engaged in flexible work, and a large number of respondents citing a search for flexible work as a major motivator to find a new job.
Competition for top performers and digital innovators demands that employers understand how much flexibility their talent pool is accustomed to and expects. Employers are wise to invest in technology, adapt policies, and train employees to create workplaces that integrate people working remotely and on-site (without overcompensating by requiring that workers spend too much time in video meetings). The survey results identify obstacles to optimal performance that underscore a need for employers to support workers with issues that interfere with effective work. Companies will want to be thoughtful about which roles can be done partly or fully remotely—and be open to the idea that there could be more of these than is immediately apparent. Employers can define the right metrics and track them to make sure the new flexible model is working.
At a more macro level, a world in which millions of people no longer routinely commute has meaningful implications for the commercial core in big urban centers and for commercial real estate overall. Likewise, such a world implies a different calculus for where Americans will live and what types of homes they will occupy. As technology emerges that eliminates the residual barriers to more distributed and asynchronous work, it could become possible to move more types of jobs overseas, with potentially significant consequences.