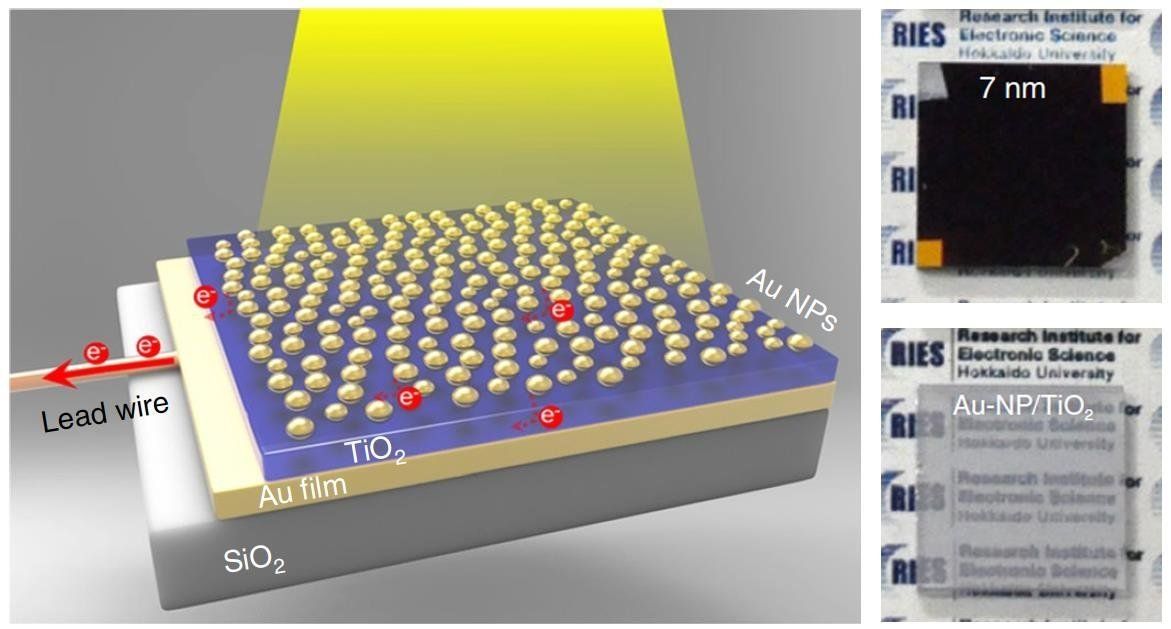
Think of the Sahara, with its windswept dunes shining in the sunlight. Some people might see barren land, with minimal water or life and scorching temperatures. Others see a potential solution to a looming energy crisis, and one that could potentially make it rain in one of the largest deserts in the world.
In a paper published this week in Science researchers found that by building out huge wind and solar farms across the desert, they could not only provide a stunning amount of power to Europe, Africa, and the Middle East, but they could simultaneously change the climate—increasing heat, but also increasing precipitation and vegetation in areas that could sorely use the added greenery. They estimate that such a venture could double the rainfall in the region, and increase vegetation cover by about 20 percent.
How much green are we talking? The Sahara covers 3.55 million square miles (9.2 million square kilometers). In the study, the researchers ran computer models that placed wind turbines across the desert close to a mile apart, and covered 20 percent of the desert with solar panels in different configurations (sometimes the panels were spread across the desert in a checkerboard pattern, and in other cases were concentrated in quadrants). Smaller coverage produced smaller climate impacts—in this case, less precipitation—but much of it depended on the location of the turbines and panels as well. For example, installing panels in the northwest corner had a larger impact than the other three desert options.
Read more