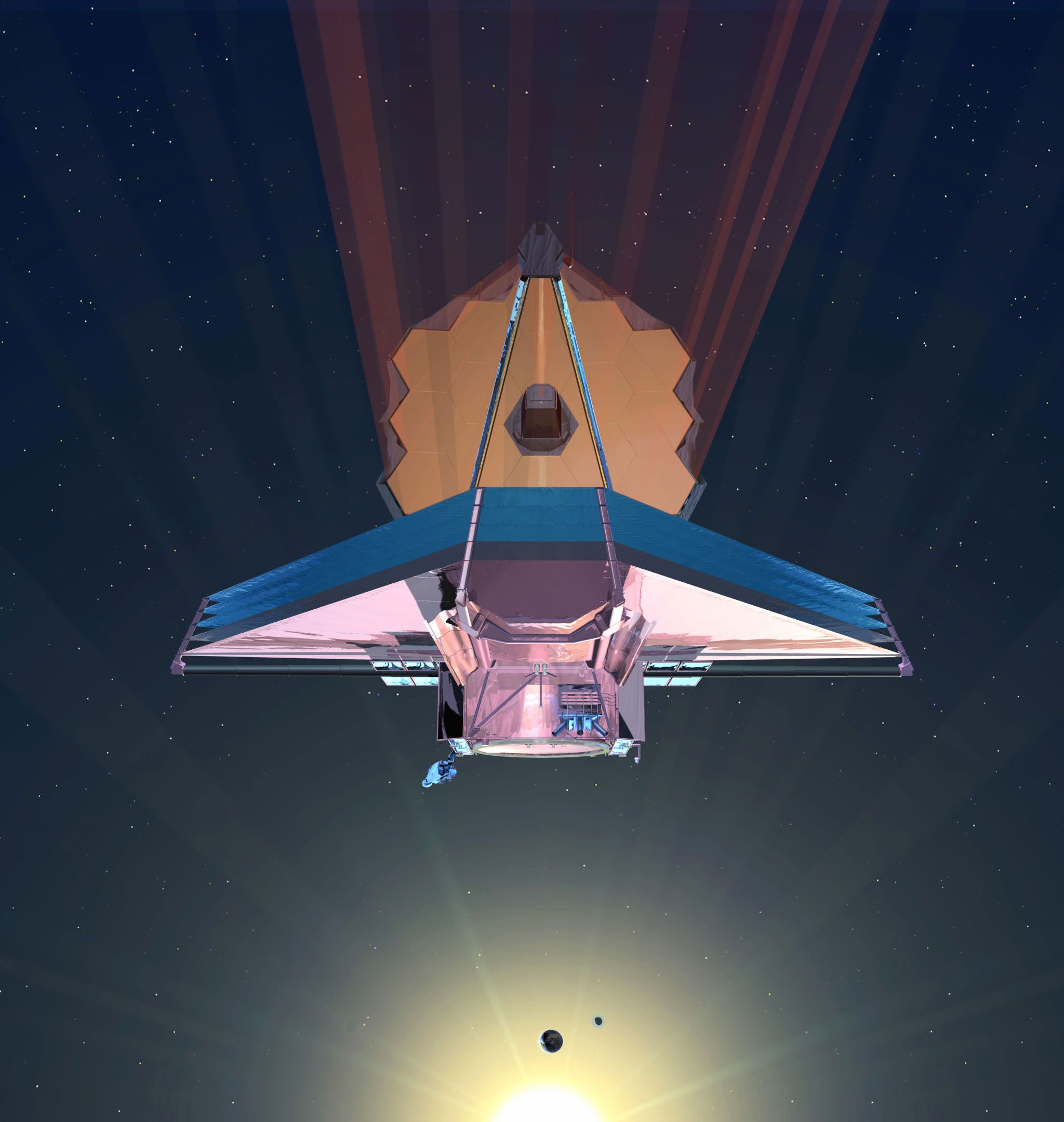
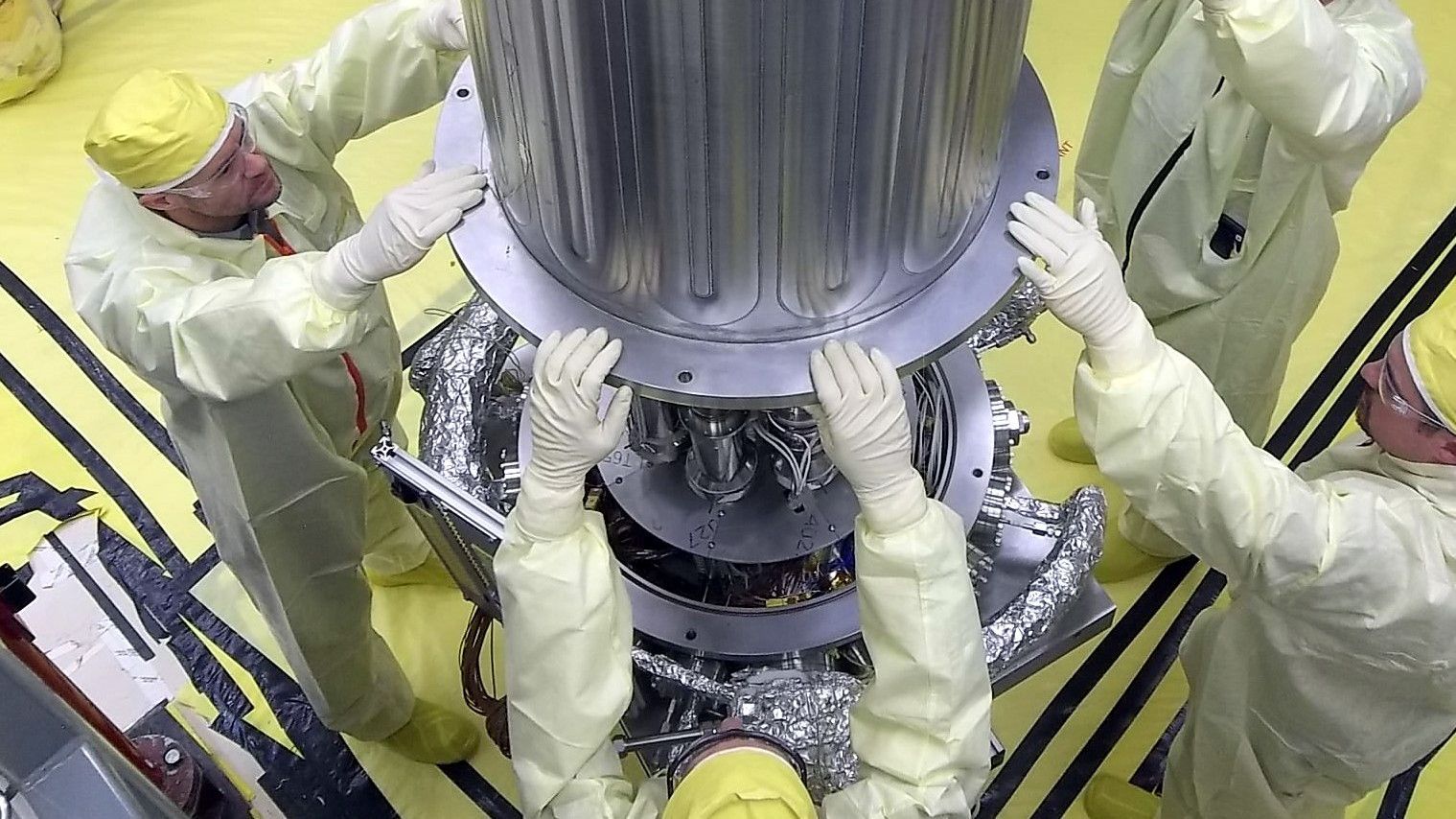
With the recent launch of the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) – which took place on Wednesday, April 18th, 2018 – a lot of attention has been focused on the next-generation space telescopes that will be taking to space in the coming years. These include not only the James Webb Space Telescope, which is currently scheduled for launch in 2020, but some other advanced spacecraft that will be deployed by the 2030s.
Such was the subject of the recent 2020 Decadal Survey for Astrophysics, which included four flagship mission concepts that are currently being studied. When these missions take to space, they will pick up where missions like Hubble, Kepler, Spitzer and Chandra left off, but will have greater sensitivity and capability. As such, they are expected to reveal a great deal more about our Universe and the secrets it holds.
As expected, the mission concepts submitted to the 2020 Decadal Survey cover a wide range of scientific goals – from observing distant black holes and the early Universe to investigating exoplanets around nearby stars and studying the bodies of the Solar System. These ideas were thoroughly vetted by the scientific community, and four have been selected as being worthy of pursuit.
Read more