Jul 6, 2017
Plasma rocket engine breakthrough as researchers solve key issue
Posted by Carse Peel in categories: innovation, particle physics
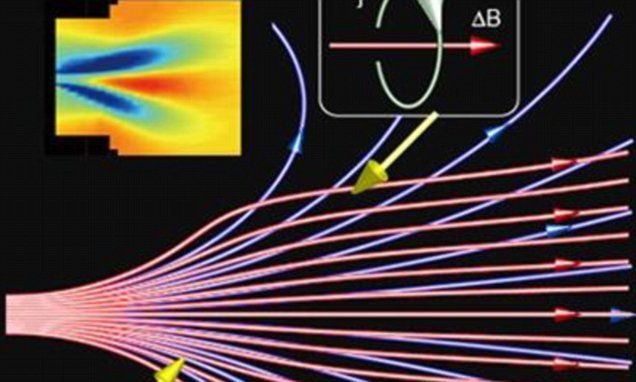
Plasma, an extremely hot gas with electrically charged particles, is found all throughout the universe and is influenced by environmental forces, such as magnetic fields.
The complex behaviours observed in space and in the lab suggest plasma can generate the magnetic field in the opposite direction to the one applied, according to the researchers from Tohoku University.
This causes the field lines to diverge, much like magnets with their North poles facing toward each other.
Continue reading “Plasma rocket engine breakthrough as researchers solve key issue” »