The concept of teleportation comes primarily from science fiction literature throughout human history, but things are changing. It’s 2015 and developments in quantum theory and general relativity physics have been successful in exploring the concept of teleportation for quite some time now.
The concept of teleportation comes primarily from science fiction literature throughout human history, but things are changing. It’s 2015 and developments in quantum theory and general relativity physics have been successful in exploring the concept of teleportation for quite some time now.
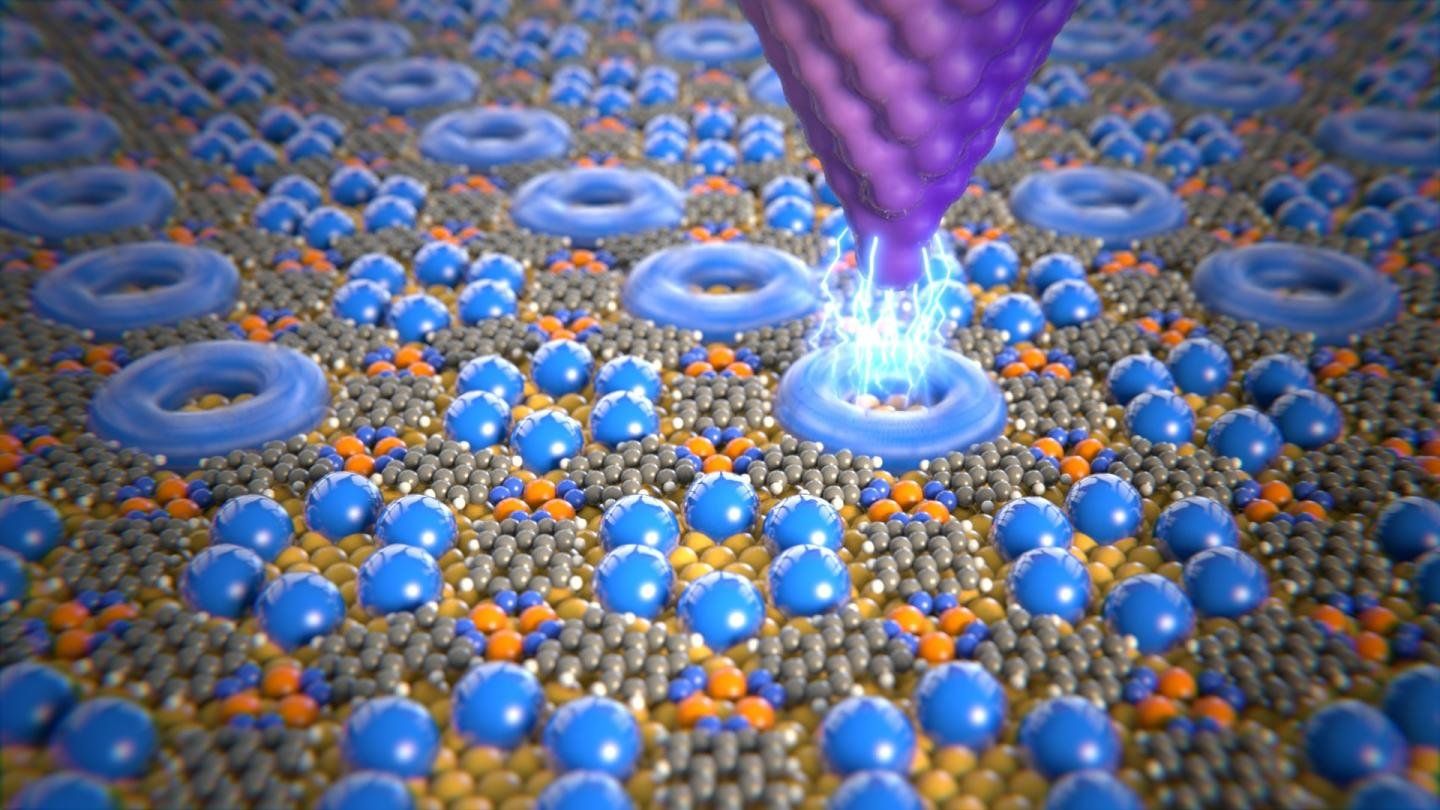
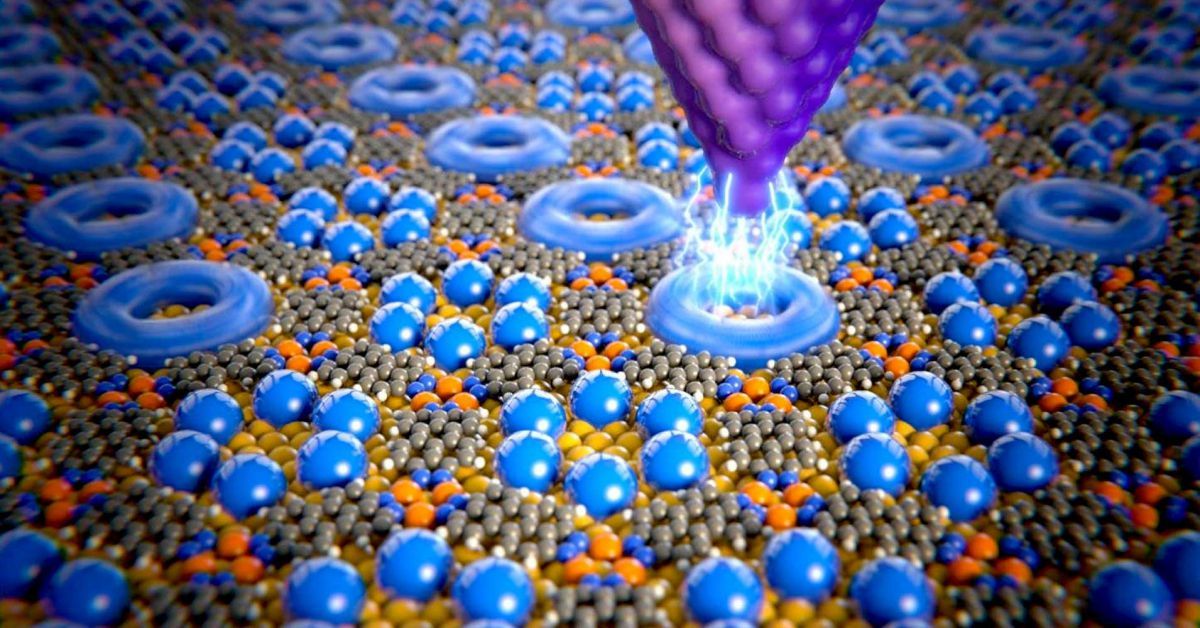
Today, numerous teleportation breakthroughs have been made. One example is the work of Professor Rainer Blatt, at the University of Innsbruck. They were successfully able to perform teleportation on atoms for the first time, their work was published in the journal Nature. They were able to transfer key properties of one particle to another without using any physical link. In this case, teleportation occurred in the form of transferring quantum states between two atoms, these include the atom’s energy, motion, magnetic field and other physical properties. This is possible due to the strange behavior that exists at the atomic scale, known as entanglement. It’s what Einstein referred to as a “spooky action.”
Another study was published by a team of University of Queensland physicists in the journal Nature in 2013 demonstrating the successful teleportation with solid state systems. A process by which, again, quantum information can be transmitted from one place to another without sending a physical carrier of information. This is the same concept, and is made possible through the phenomenon of entanglement.
Continue reading “Scientists Report Teleportation of Physical Objects From One Location To Another” »