Oct 13, 2023
Surprising discovery shows electron beam radiation can repair nanostructures
Posted by Paul Battista in categories: chemistry, nanotechnology
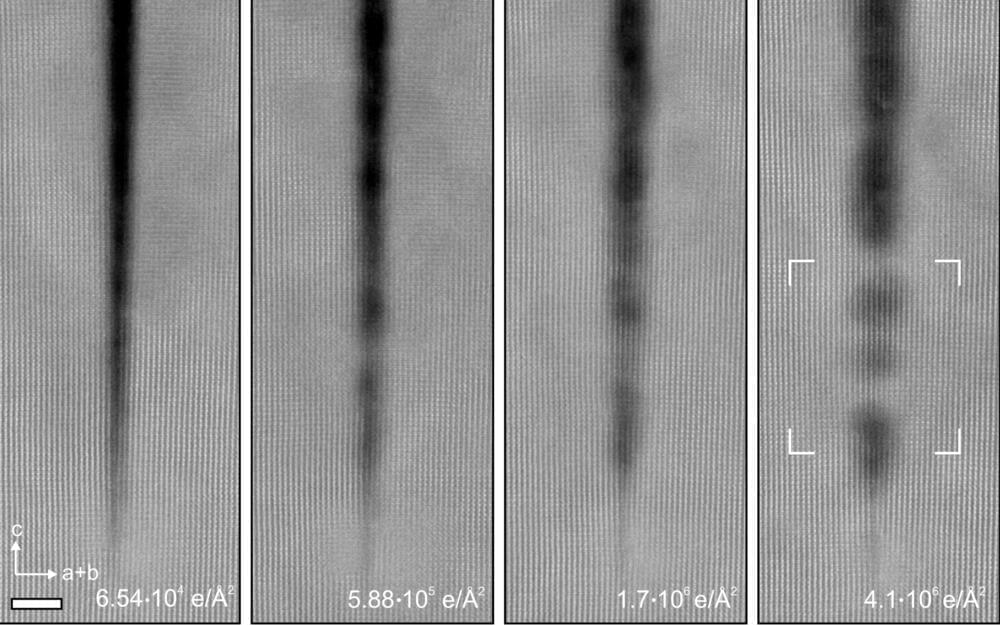
In a surprising new study, researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities have found that the electron beam radiation that they previously thought degraded crystals can actually repair cracks in these nanostructures.
The groundbreaking discovery provides a new pathway to create more perfect crystal nanostructures, a process that is critical to improving the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of materials that are used in virtually all electronic devices we use every day.
“For a long time, researchers studying nanostructures were thinking that when we put the crystals under electron beam radiation to study them that they would degrade,” said Andre Mkhoyan, a University of Minnesota chemical engineering and materials science professor and lead researcher in the study. “What we showed in this study is that when we took a crystal of titanium dioxide and irradiate it with an electron beam, the naturally occurring narrow cracks actually filled in and healed themselves.”