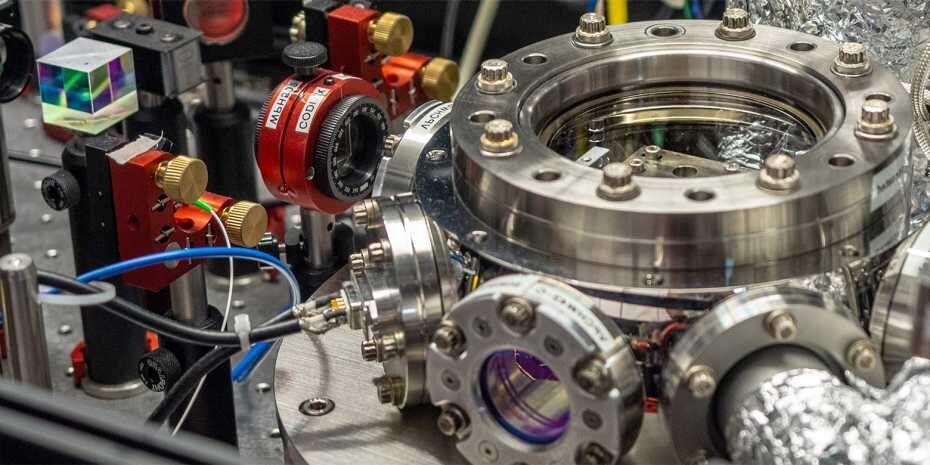
ETH researchers have cooled a nanoparticle to a record low temperature, thanks to a sophisticated experimental set-up that uses scattered laser light for cooling. Until now, no one has ever cooled a nanoparticle to such low temperatures in a photon cage. Dominik Windey and René Reimann – a doctoral student and postdoc in the group led by Lukas Novotny, Professor of Photonics – have succeeded in cooling a 140 nanometre glass bead down to a few thousandths of a degree above absolute zero.
The researchers recently published details of their work in the journal Physical Review Letters. Their breakthrough came in the form of a sophisticated experimental set-up involving optical tweezers, whereby a nanoparticle can be made to levitate with the aid of a laser beam. The group has already used the same optical tweezers in previous work, in which they caused a nanoparticle to rotate around its own axis at extremely high speed.