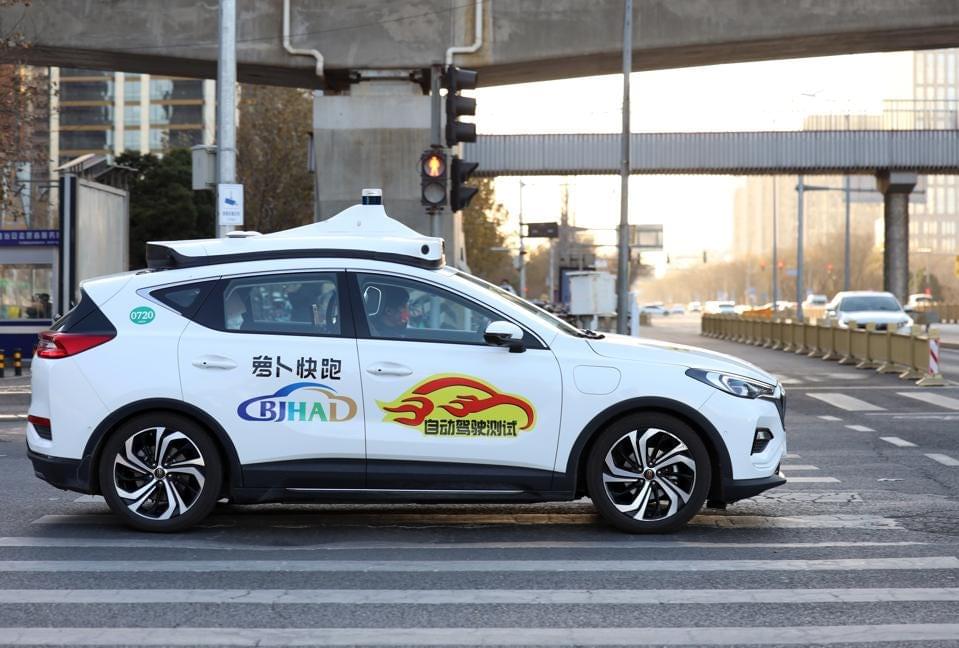
More than a score of companies are pushing to be early winners in the race for self-driving taxis — robotaxis — with the potential that brings to capture the entire value chain of car transport from your riders. They are all at different stages, and they almost all want to convince the public and investors that they are far along.
To really know how far along a project is, you need the chance to look inside it. To see the data only insiders see on just how well their vehicle is performing, as well as what it can and can’t do. Most teams want to keep those inside details secret, though in time they will need to reveal them to convince the public, and eventually regulators that they are ready to deploy.
Because they keep them secret, those of us looking in from the outside can only scrape for clues. The biggest clues come when they reach certain milestones, and when they take risks which tell us their own internal math has said it’s OK to take that risk. Most teams announce successes and release videos of drives, but these offer us only limited information because they can be cherry picked. The best indicators are what they do, not what they say.