Feb 28, 2019
Researchers develop a fleet of 16 miniature cars for cooperative driving experiments
Posted by Quinn Sena in categories: information science, robotics/AI, transportation
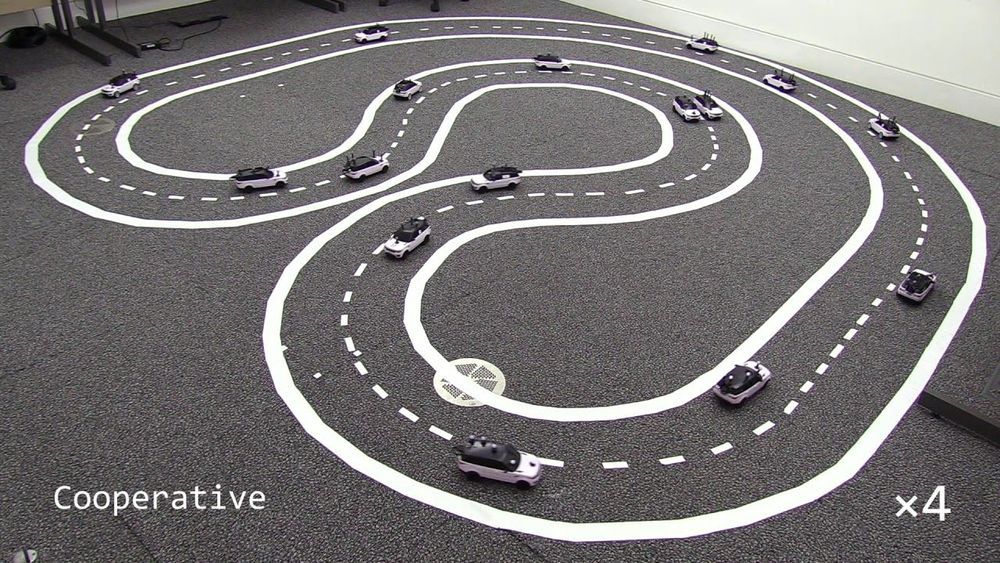
A team of researchers at The University of Cambridge has recently introduced a unique experimental testbed that could be used for experiments in cooperative driving. This testbed, presented in a paper pre-published on arXiv, consists of 16 miniature Ackermann-steering vehicles called Cambridge Minicars.
“Using true-scale facilities for vehicle testbeds is expensive and requires a vast amount of space,” Amanda Prorok. “Our main objective was to build a low-cost, multi-vehicle experimental setup that is easy to maintain and that is easy to use to prototype new autonomous driving algorithms. In particular, we were interested in testing and tangibly demonstrating the benefits of cooperative driving on multi-lane road topographies.”