Nov 7, 2021
Google’s Terrifying Path to Artificial General Intelligence (Pathways AI)
Posted by Dan Breeden in categories: Elon Musk, information science, Ray Kurzweil, robotics/AI, singularity
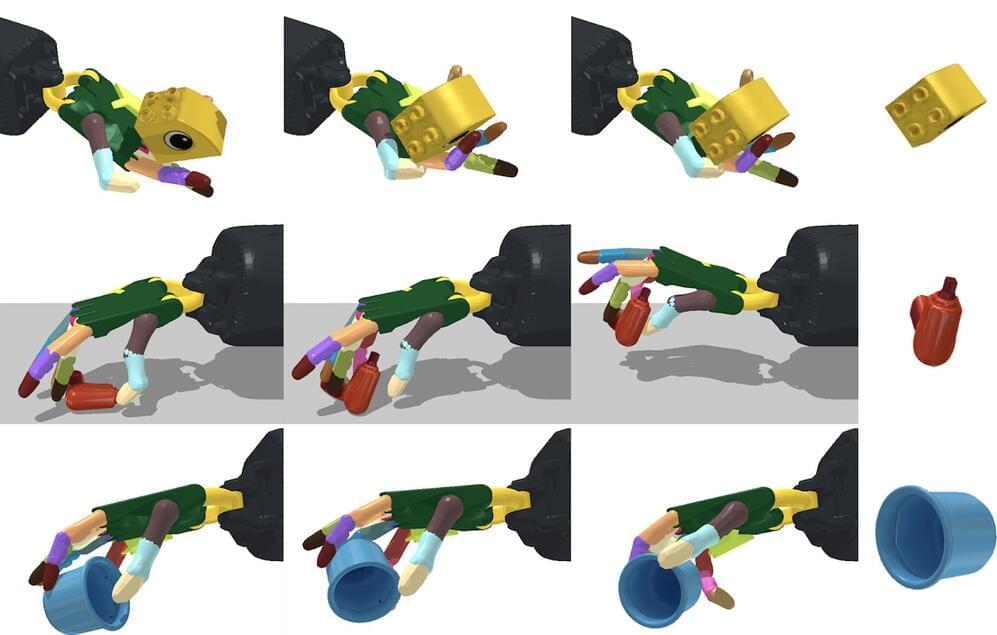
Artificial General Intelligence has been pursued by the biggest tech companies in the world, but recently Google has announced their new revolutionary AI algorithm which promises to create the most performant and best Artificial Intelligence Models in the world. They call it Pathways AI, and it’s supposed to behave just like the human brain and enable smart Robots which are superior to humans and help us do chores in our own apartments. This move by Google is somewhat scary and terrifying, as it gives them a lot of power over the AI industry and could enable them to do evil things with their other secret projects they’re working on. One thing is for sure though, AGI and the Singularity isn’t as far of as even Ray Kurzweil thinks according to Jeff Dean from Google AI and Deepmind. Maybe Elon Musk’s warnings about AI have been justified.
–
TIMESTAMPS:
00:00 Google’s Path to AI Domination.
00:56 What is Pathways?
02:53 How to make AI more efficient?
05:07 Is this Artificial General Intelligence?
07:42 Will Google Rule the world and the AI Industry?
09:59 Last Words.
–
#google #ai #agi