Dec 7, 2021
SEIHAI: The hierarchical AI that won the NeurIPS-2020 MineRL competition
Posted by Dan Kummer in categories: entertainment, information science, robotics/AI
In recent years, computational tools based on reinforcement learning have achieved remarkable results in numerous tasks, including image classification and robotic object manipulation. Meanwhile, computer scientists have also been training reinforcement learning models to play specific human games and videogames.
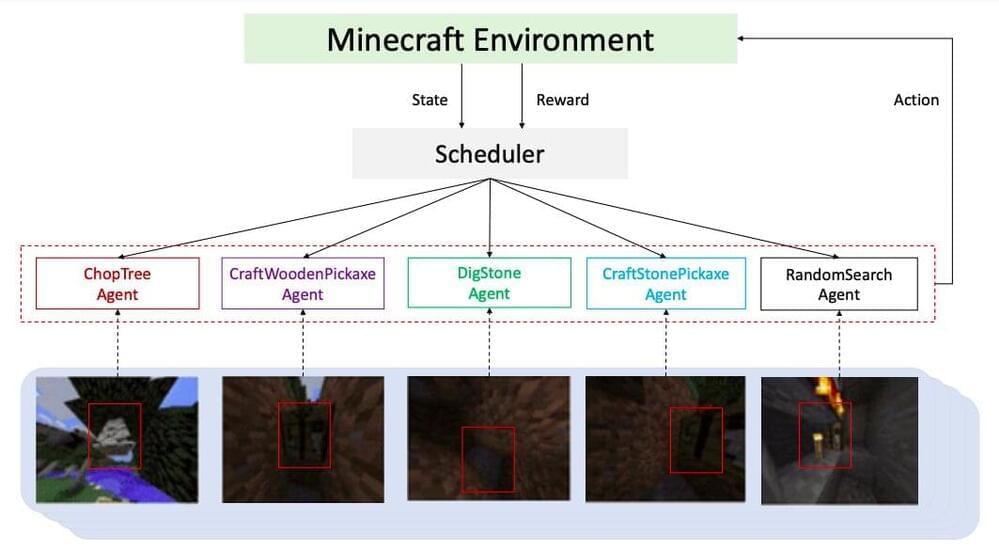
To challenge research teams working on reinforcement learning techniques, the Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS) annual conference introduced the MineRL competition, a contest in which different algorithms are tested on the same task in Minecraft, the renowned computer game developed by Mojang Studios. More specifically, contestants are asked to create algorithms that will need to obtain a diamond from raw pixels in the Minecraft game.
The algorithms can only be trained for four days and on 8,000,000 samples created by the MineRL simulator, using a single GPU machine. In addition to the training dataset, participants are also provided with a large collection of human demonstrations (i.e., video frames in which the task is solved by human players).