Mar 22, 2024
Genetic Modification of Brain Organoids
Posted by Dan Breeden in categories: biotech/medical, evolution, genetics, neuroscience
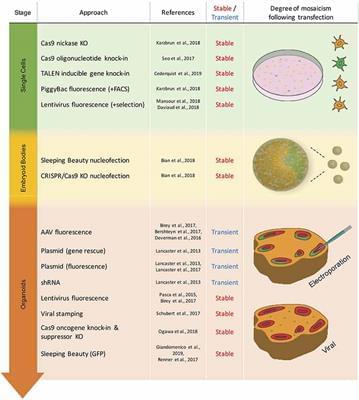
Brain organoids have become increasingly used systems allowing 3D-modeling of human brain development, evolution, and disease. To be able to make full use of these modeling systems, researchers have developed a growing toolkit of genetic modification techniques. These techniques can be applied to mature brain organoids or to the preceding embryoid bodies (EBs) and founding cells. This review will describe techniques used for transient and stable genetic modification of brain organoids and discuss their current use and respective advantages and disadvantages. Transient approaches include adeno-associated virus (AAV) and electroporation-based techniques, whereas stable genetic modification approaches make use of lentivirus (including viral stamping), transposon and CRISPR/Cas9 systems. Finally, an outlook as to likely future developments and applications regarding genetic modifications of brain organoids will be presented.
The development of brain organoids (Kadoshima et al., 2013; Lancaster et al., 2013) has opened up new ways to study brain development and evolution as well as neurodevelopmental disorders. Brain organoids are multicellular 3D structures that mimic certain aspects of the cytoarchitecture and cell-type composition of certain brain regions over a particular developmental time window (Heide et al., 2018). These structures are generated by differentiation of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) or embryonic stem cells (ESCs) into embryoid bodies followed by, or combined, with neural induction (Kadoshima et al., 2013; Lancaster et al., 2013). In principle, two different classes of brain organoid protocols can be distinguished, namely: (i) the self-patterning protocols which produce whole-brain organoids; and (ii) the pre-patterning protocols which produce brain region-specific organoids (Heide et al., 2018).