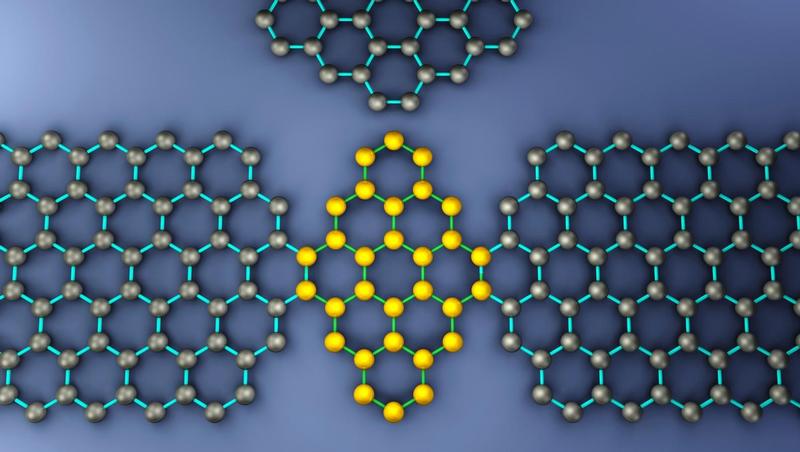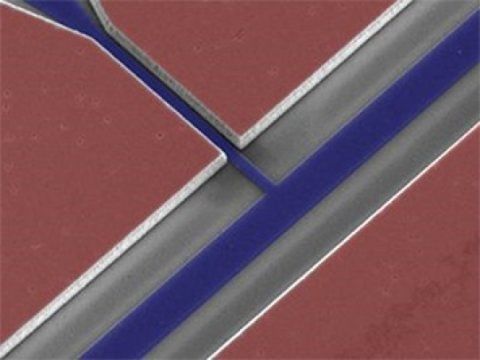
If biochemists had access to a quantum computer, they could perfectly simulate the properties of new molecules to develop drugs in ways that would take today’s fastest computers decades. A new device takes us closer to providing such a computer. The device successfully traps, detects, and manipulates an ensemble of electrons above the surface of superfluid helium. The system integrates a nanofluidic channel with a superconducting circuit.
Because they are so small, electrons normally interact weakly with electrical signals. The new device, however, gives the electron more time to interact, and it is this setup that makes it possible to build a qubit, the quantum computing equivalent of a bit. Quantum computers could provide the necessary computing power to model extremely large and complex situations in physics, biology, weather systems and many others.
While isolated electrons in a vacuum can store quantum information nearly perfectly, in real materials, the movements of surrounding atoms disturbs them, eventually leading to the loss of information. This work is a step towards realizing isolated, trapped single electrons by taking advantage of the unique relationship existing between electrons and superfluid helium. Electrons will levitate just above the surface of helium, about 10 nanometers away, insensitive to the atomic fluctuations below. While this effect has been known, holding them in a superconducting device structure has not been demonstrated before this work. At the heart of this new technology is a resonator based on circuit quantum electrodynamics (cQED) architecture, which provides a path to trap electrons above helium and detect the spins of the electrons. Because they are so small, electrons normally interact only very weakly with electrical signals.
Read more