Archive for the ‘computing’ category: Page 761
Aug 4, 2016
New microfluidic chip replicates muscle-nerve connection
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: bioengineering, biotech/medical, computing, genetics, neuroscience
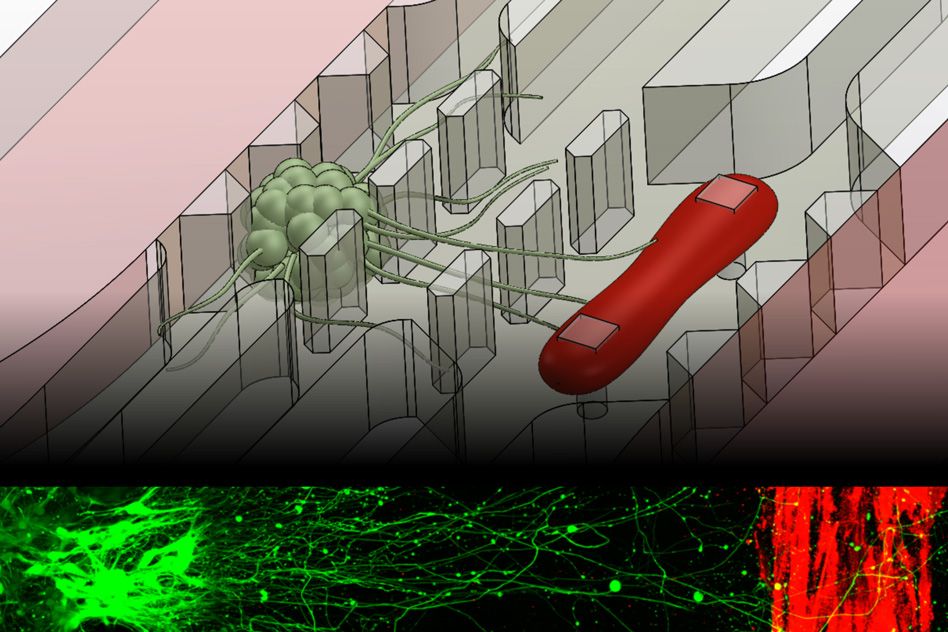
MIT engineers have developed a microfluidic device that replicates the neuromuscular junction—the vital connection where nerve meets muscle. The device, about the size of a U.S. quarter, contains a single muscle strip and a small set of motor neurons. Researchers can influence and observe the interactions between the two, within a realistic, three-dimensional matrix.
The researchers genetically modified the neurons in the device to respond to light. By shining light directly on the neurons, they can precisely stimulate these cells, which in turn send signals to excite the muscle fiber. The researchers also measured the force the muscle exerts within the device as it twitches or contracts in response.
The team’s results, published online today in Science Advances, may help scientists understand and identify drugs to treat amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), more commonly known as Lou Gehrig’s disease, as well as other neuromuscular-related conditions.
Continue reading “New microfluidic chip replicates muscle-nerve connection” »
Aug 3, 2016
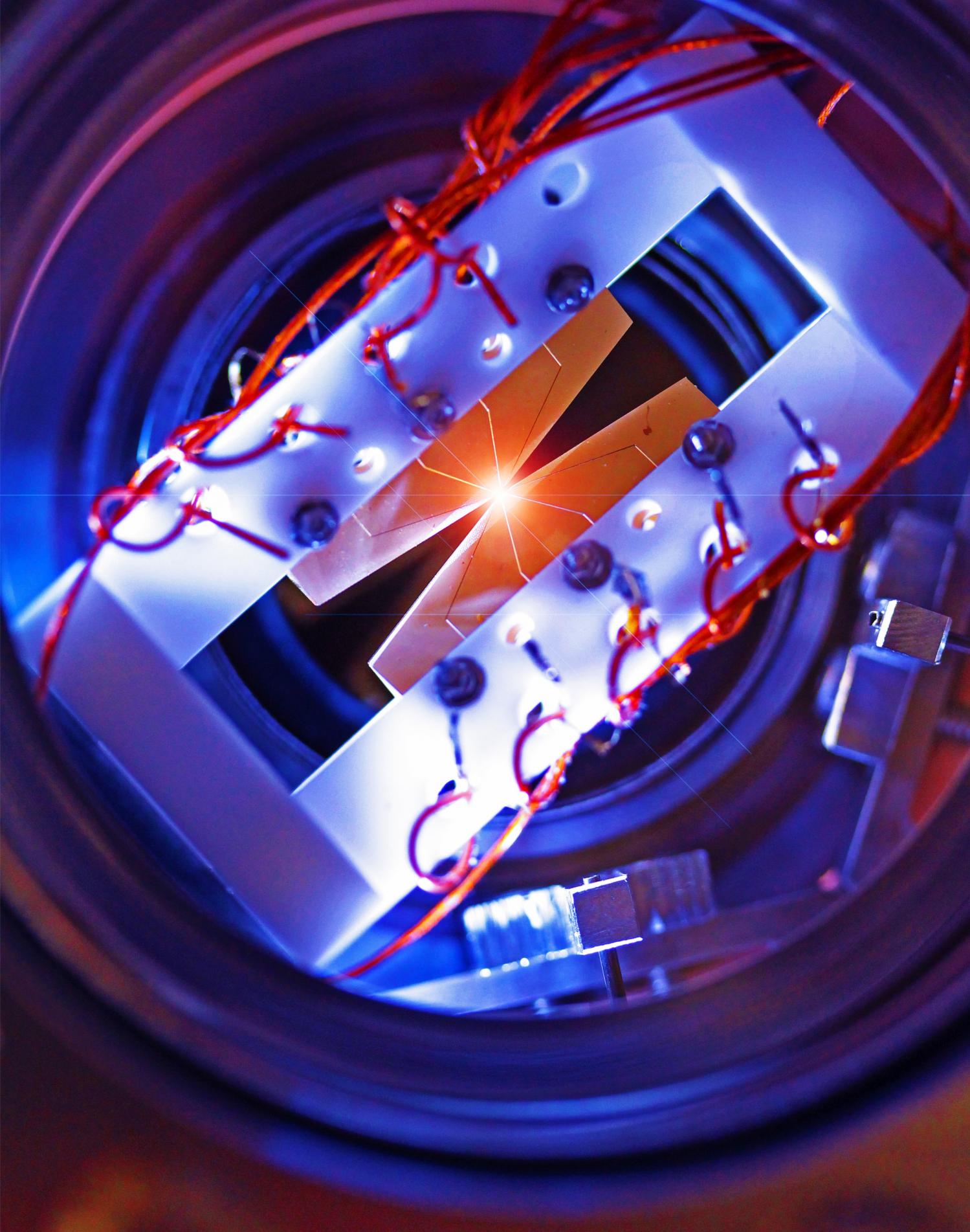
Programmable ions set the stage for general-purpose quantum computers
Posted by Andreas Matt in categories: computing, information science, particle physics, quantum physics
Quantum computers promise speedy solutions to some difficult problems, but building large-scale, general-purpose quantum devices is a problem fraught with technical challenges.
To date, many research groups have created small but functional quantum computers. By combining a handful of atoms, electrons or superconducting junctions, researchers now regularly demonstrate quantum effects and run simple quantum algorithms —small programs dedicated to solving particular problems.
But these laboratory devices are often hard-wired to run one program or limited to fixed patterns of interactions between the quantum constituents. Making a quantum computer that can run arbitrary algorithms requires the right kind of physical system and a suite of programming tools. Atomic ions, confined by fields from nearby electrodes, are among the most promising platforms for meeting these needs.
Continue reading “Programmable ions set the stage for general-purpose quantum computers” »
Aug 3, 2016
Quantum Computing Just Grew Way the Hell Up
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: computing, information science, quantum physics
Additional insights on the latest reprogrammable QC.
Researchers implement a key piece of Shor’s algorithm in a programmable quantum computer.
Aug 3, 2016
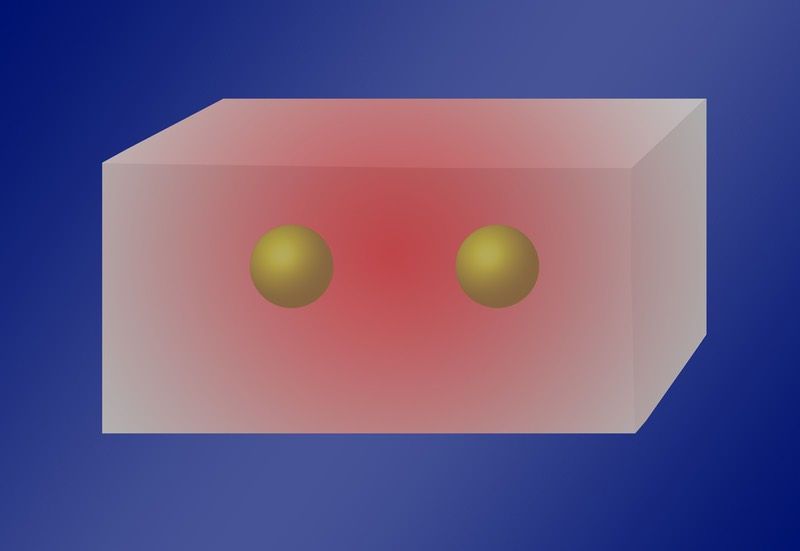
How it works: The first programmable quantum computer module based on ions
Posted by Bruno Henrique de Souza in categories: computing, quantum physics
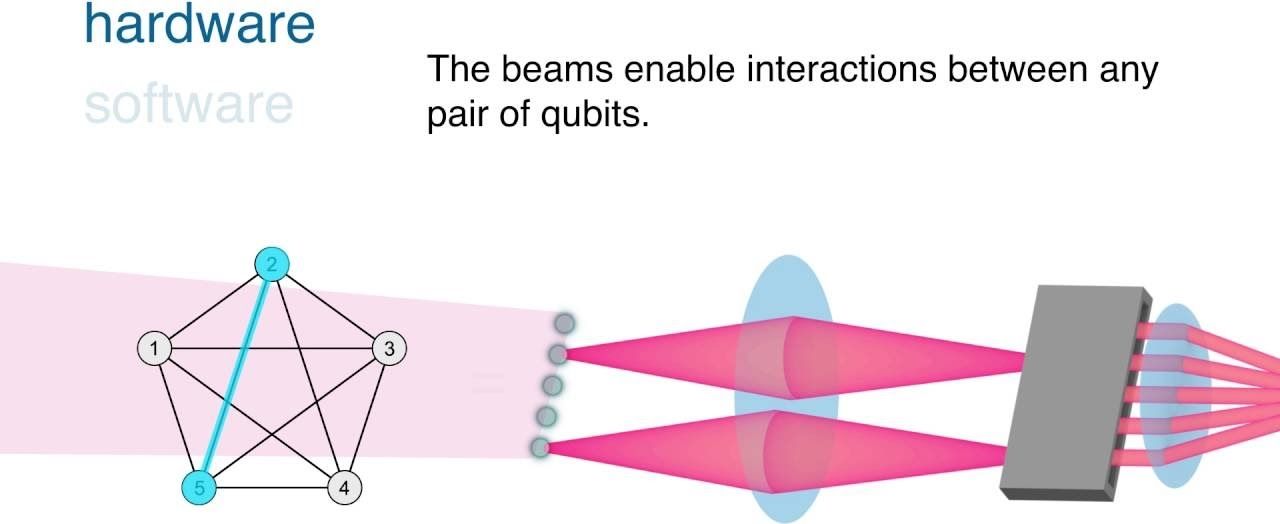
O primeiro totalmente reconfigurável e programável módulo de computador qu ntico.
Joint Quantum Institute http://goo.gl/dc6z4a
Aug 2, 2016
How computer algorithms shape our experience of the real world
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: computing, information science, robotics/AI, singularity
Interesting and true on many situations; and will only expand as we progress in areas of AI, QC, and Singularity as well.
The use of algorithms to filter and present information online is increasingly shaping our everyday experience of the real world, a study published by Information, Communication & Society argues.
Associate Professor Michele Willson of Curtin University, Perth, Australia looked at particular examples of computer algorithms and the questions they raise about personal agency, changing world views and our complex relationship with technologies.
Continue reading “How computer algorithms shape our experience of the real world” »
Aug 2, 2016
Computers will be able to assess humans’ state of mind
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: biotech/medical, computing, robotics/AI, security
I see many uses for this such as provider services including front office & hospital admissions, security in assessing people in line or trying to gain entry, etc.
Machines are taking over more and more tasks. Ideally, they should also be capable to support the human in case of poor performance. To intervene appropriately, the machine should understand what is going on with the human. Fraunhofer scientists have developed a diagnostic tool that recognizes user states in real time and communicates them to the machine.
The camera firmly focuses on the driver’s eyes. If they are closed for more than one second, an alarm is triggered. This technique prevents the dangerous micro-sleep at the wheel. “It is not always as easy for a machine to detect what state the human is in, as it is in this case,” says Jessica Schwarz from the Fraunhofer Institute for Communication, Information Processing and Ergonomics FKIE in Wachtberg, just south of Bonn.
Continue reading “Computers will be able to assess humans’ state of mind” »
Aug 2, 2016
Dubai to become an international 3D printing hub
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: 3D printing, computing
Impressive.
3D printing services will grow from $2.5bn in 2013 to $16.2bn in 2018, according to Canalys Tags: 3D printing, Cloud computing.
Aug 2, 2016
Virtual Light Particles May Boost Quantum Computing
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: computing, particle physics, quantum physics
A single photon can excite two or more atoms at the same time, scientists found. And the light particle would do so in a very counterintuitive way, by summoning one or more companion photons out of nothingness.
If you think of particles of light, or photons, as billiard balls, it makes intuitive sense that a single photon can excite a single atom.
The new, less intuitive finding depends on the strange nature of quantum mechanics, and might help improve advanced machines known as quantum computers, researchers said. Prior work suggested that such machines could simultaneously perform more calculations in one instant than there are atoms in the universe. [Warped Physics: 10 Effects of Faster-than-Light Travel].
Continue reading “Virtual Light Particles May Boost Quantum Computing” »
Aug 2, 2016
Most Powerful Quantum Optimization Processor Worldwide Now Online at USC ISI
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: computing, quantum physics
More on the new most powerful QC at USC.
Following a recent upgrade, the USC-Lockheed Martin Quantum Computing Center (QCC) based at the USC Information Sciences Institute (ISI) with 1098 qubits, is now the leader in qubit capacity…
USC Viterbi School of Engineering Amy Blumenthal, 917.710.1897 amyblume@usc.edu