As our lives become increasingly intertwined with technology—whether supporting communication while working remotely or streaming our favorite show—so too does our reliance on the data these devices create. Data centers supporting these technology ecosystems produce a significant carbon footprint—and consume 200 terawatt hours of energy each year, greater than the annual energy consumption of Iran. To balance ecological concerns yet meet growing demand, advances in microelectronic processors—the backbone of many Internet of Things (IoT) devices and data hubs—must be efficient and environmentally friendly.
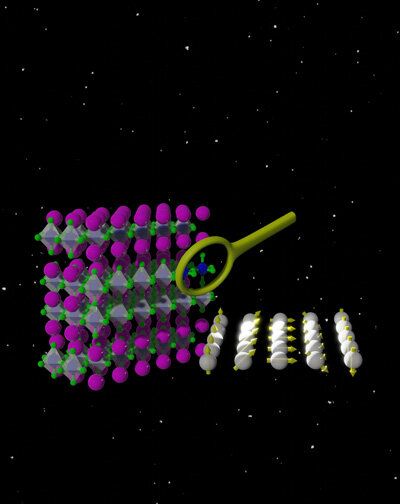
Northwestern University materials scientists have developed new design principles that could help spur development of future quantum materials used to advance (IoT) devices and other resource-intensive technologies while limiting ecological damage.
“New path-breaking materials and computing paradigms are required to make data centers more energy-lean in the future,” said James Rondinelli, professor of materials science and engineering and the Morris E. Fine Professor in Materials and Manufacturing at the McCormick School of Engineering, who led the research.