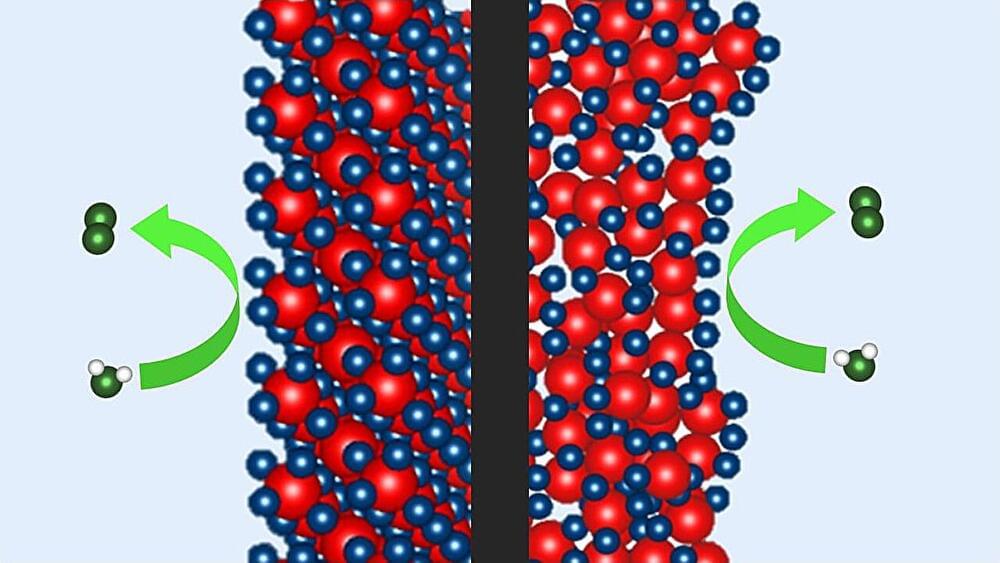
Iridium-based catalysts are needed to produce hydrogen using water electrolysis. Now, a team at HZB has shown that the newly developed P2X catalyst, which requires only a quarter of the iridium, is as efficient and stable over time as the best commercial catalyst. Measurements at BESSY II have now revealed how the special chemical environment in the P2X catalyst during electrolysis promotes the oxygen evolution reaction during water splitting.
In the future, hydrogen will be needed in a climate-neutral energy system to store energy, as a fuel, and a raw material for the chemical industry. Ideally, it should be produced in a climate-neutral way, using electricity generated from harnessing the sun’s or wind energy, via the electrolysis of water.
In that respect, Proton Exchange Membrane Water Electrolysis (PEM-WE) is currently considered a key technology. Both electrodes are coated with special electrocatalysts to accelerate the desired reaction. Iridium-based catalysts are best suited for the anode, where the sluggish oxygen evolution reaction occurs. However, iridium is one of the rarest elements on earth, and one of the major challenges is to significantly reduce the demand for this precious metal.