Apr 10, 2022
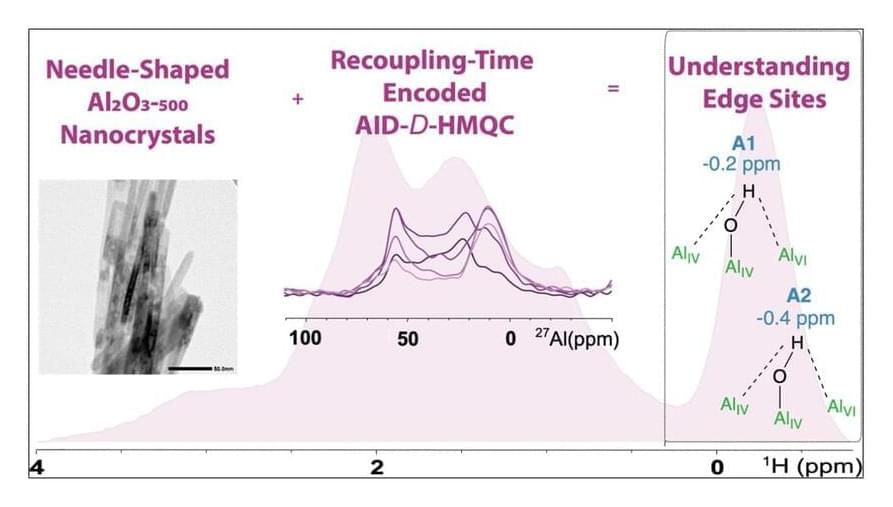
Revisiting Edge Sites of γ-Al2O3 Using Needle-Shaped Nanocrystals and Recoupling-Time-Encoded {27Al}-1H D-HMQC NMR Spectroscopy
Posted by Shubham Ghosh Roy in categories: chemistry, quantum physics
Despite being widely used in numerous catalytic applications, our understanding of reactive surface sites of high-surface-area γ-Al2O3 remains limited to date. Recent contributions have pointed toward the potential role of highly reactive edge sites contained in the high-field signal (−0.5 to 0 ppm) of the 1H NMR spectrum of γ-Al2O3 materials. This work combines the development of well-defined, needle-shaped γ-Al2O3 nanocrystals having a high relative fraction of edge sites with the use of state-of-the-art solid-state NMR to significantly deepen our understanding of this specific signal. We are able to resolve two hydroxyl sites with distinct isotropic chemical shifts of −0.2 and −0.4 ppm and different positions within the dipole–dipole network from 1H–1H single-quantum double-quantum NMR.