Oct 30, 2024
Machine Learning Meets Nanotech: Caltech’s Breakthrough in Mass Spectrometry
Posted by Paul Battista in categories: biotech/medical, nanotechnology, robotics/AI
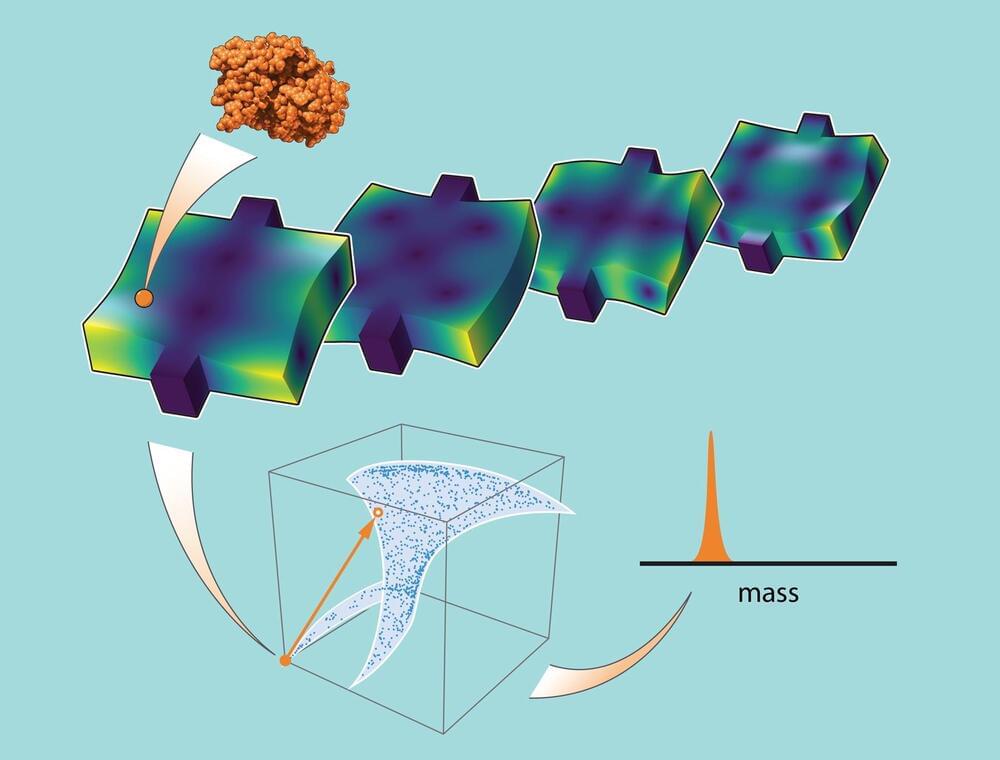
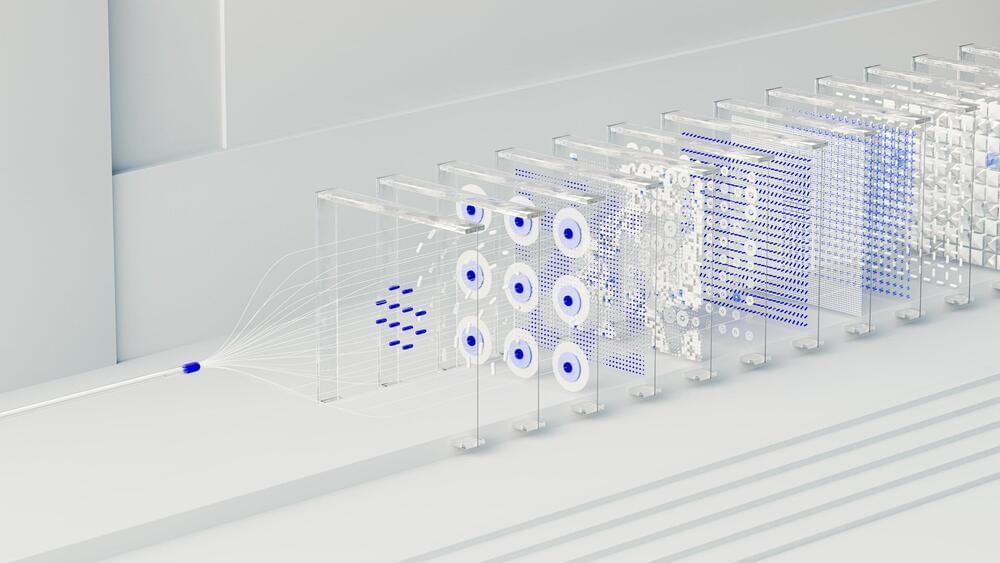
Caltech scientists have introduced a revolutionary machine-learning-driven technique for accurately measuring the mass of individual particles using advanced nanoscale devices.
This method could dramatically enhance our understanding of proteomes by allowing for the mass measurement of proteins in their native forms, thus offering new insights into biological processes and disease mechanisms.
Caltech scientists have developed a machine-learning-powered method that enables precise measurement of individual particles and molecules using advanced nanoscale devices. This breakthrough could lead to the use of various devices for mass measurement, which is key to identifying proteins. It also holds the potential to map the complete proteome—the full set of proteins in an organism.