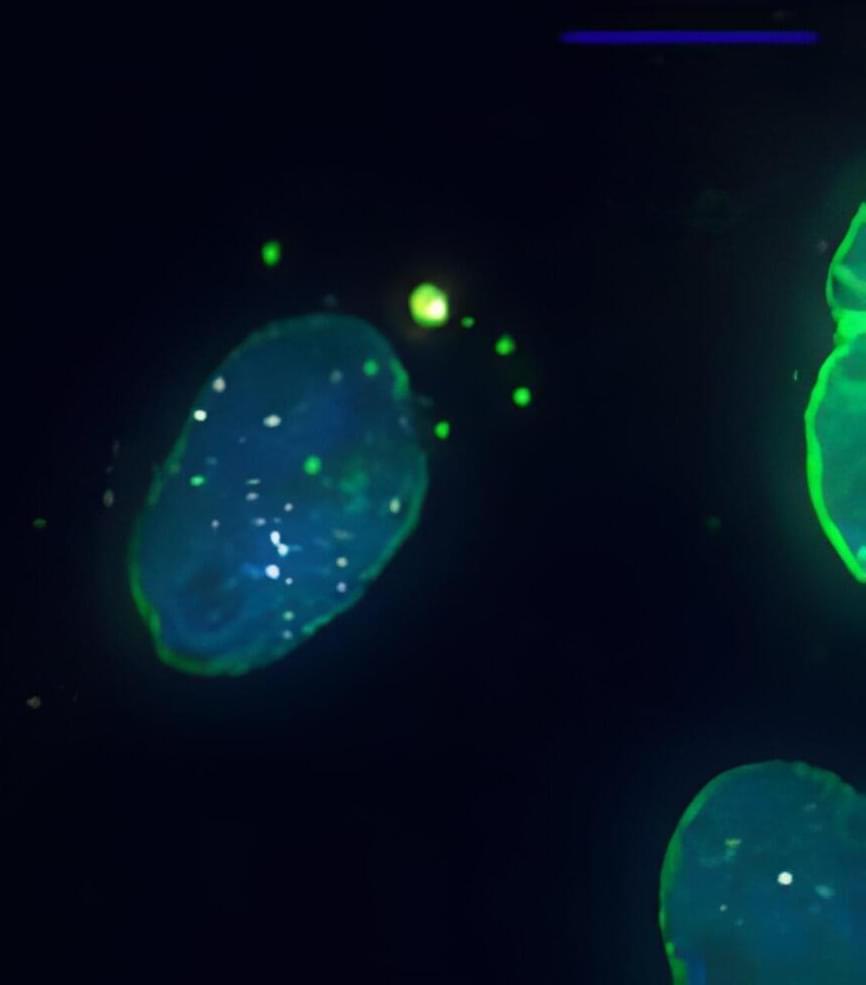
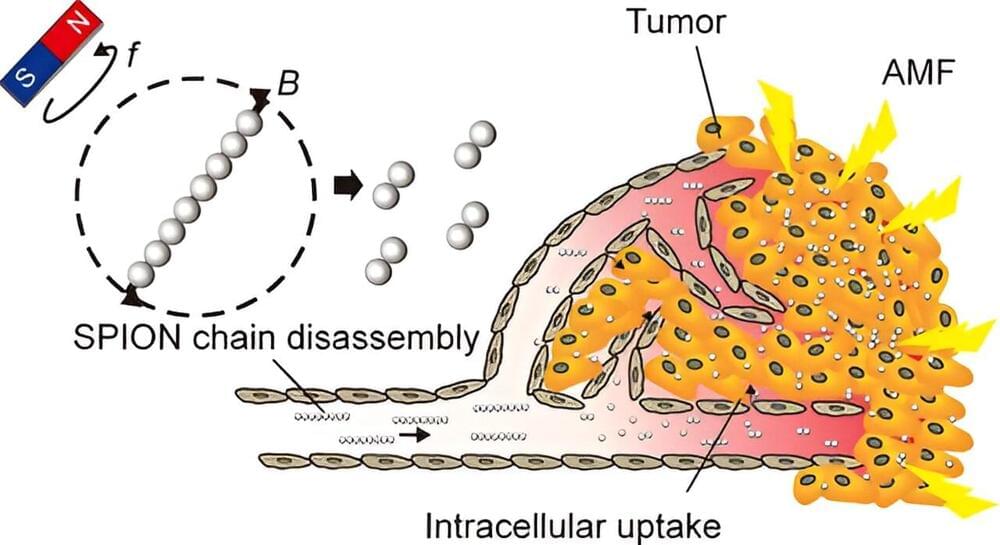
In the biomedical field, optical characterization of cells and tissues is a valuable tool for understanding physiological mechanisms. Current biomedical optical imaging techniques include fluorescence imaging [1], confocal microscopy [2], optical coherence tomography [3], two-photon microscopy [4], near-infrared spectroscopy [5], and diffuse optical tomography [6]. These techniques have significantly advanced biomedical technology and are widely used for both preclinical and clinical purposes. However, the strong optical scattering within turbid biological tissues fundamentally limits the imaging depth of these pure optical imaging techniques to no deeper than the optical ballistic depth ( 1 mm). Thus, their observation depth is superficial and other imaging modalities are needed to explore deeper layers of biological tissue [7].
Photoacoustic imaging (PAI), a promising biomedical technique, achieves superior imaging depths by forming images from optically-derived acoustic signals, which inherently attenuate less than optical signals in biological tissue [8, 9, 10]. PAI is based on the photoacoustic (PA) effect, in which energy is converted from light to acoustic waves via thermoelastic expansion [11,12,13,14,15,16]. To generate PA waves, a laser beam with a typical pulse width of a few nanoseconds illuminates the target tissue. The optical chromophores in biological tissue absorb the light energy and then release the energy soon after. The energy release can can occur as either light energy with a slightly shifted wavelength or as thermal energy that causes thermoelastic expansion. In PAI, the rapidly alternating thermoelastic expansion and contraction caused by pulsed light illumination generates vibrations in tissue that propagate as acoustic waves called PA waves. The generated PA waves can be detected by conventional ultrasound (US) transducers for image generation. Because PAI and ultrasound imaging (USI) share the same signal reception and image reconstruction principle, the two modalities are technically fully compatible and can be implemented in a single US imaging platform accompanied with pulse laser source [17,18,19,20,21]. Since PAI can capture the photochemical properties of the target site, combining PAI with USI can provide both chemical and structural information about a target tissue.
One distinctive advantage of PAI is that its resolution and imaging depth can be adjusted to suit a specific target area. The resolution of PA signals depends on both the optical focus of the excitation laser and the acoustic focus of the receiving US transducer [22], so images with tuned spatial resolutions and imaging depths can be achieved by modifying the system configuration [23]. PAI’s wide applications to date have included nanoscale surface and organelle imaging [24,25,26,27,28], microscale cellular imaging [29,30,31,32], macroscale small animal imaging [33,34,35], and clinical human imaging [36,37,38].

 150 YEARS MAXIMUM BIOLOGICAL AGE — “We observed, that the age-dependent population DOSI distribution broadening could be explained by a progressive loss of physiological resilience measured by the DOSI auto-correlation time. Extrapolation of this trend suggested that DOSI recovery time and variance would simultaneously diverge at a critical point of 120 − 150 years of age corresponding to a complete loss of resilience. The observation was immediately confirmed by the independent analysis of correlation properties of intraday physical activity levels fluctuations collected by wearable devices. We conclude that the criticality resulting in the end of life is an intrinsic biological property of an organism that is independent of stress factors and signifies a fundamental or absolute limit of human lifespan.”
150 YEARS MAXIMUM BIOLOGICAL AGE — “We observed, that the age-dependent population DOSI distribution broadening could be explained by a progressive loss of physiological resilience measured by the DOSI auto-correlation time. Extrapolation of this trend suggested that DOSI recovery time and variance would simultaneously diverge at a critical point of 120 − 150 years of age corresponding to a complete loss of resilience. The observation was immediately confirmed by the independent analysis of correlation properties of intraday physical activity levels fluctuations collected by wearable devices. We conclude that the criticality resulting in the end of life is an intrinsic biological property of an organism that is independent of stress factors and signifies a fundamental or absolute limit of human lifespan.”