Jul 17, 2020
Sperm discovery reveals clue to genetic ‘immortality’
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: biotech/medical, genetics, life extension
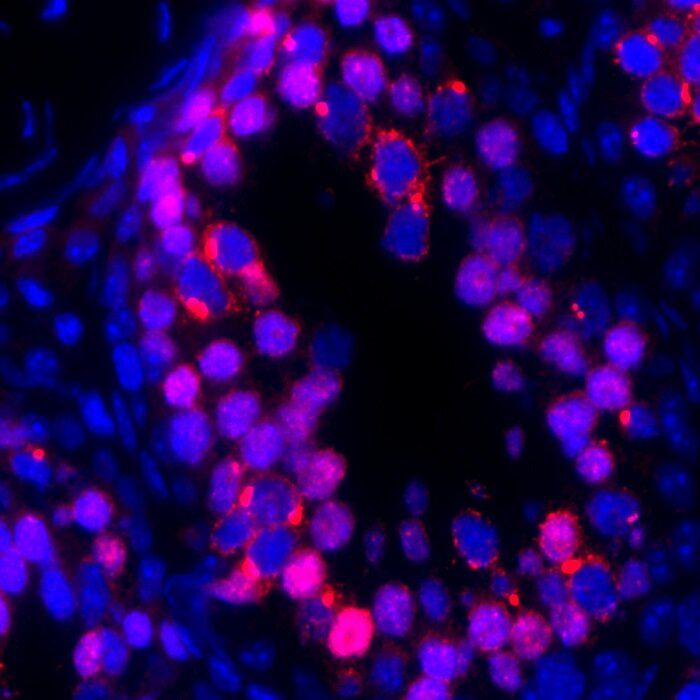
New insights into an elusive process that protects developing sperm cells from damage in growing embryos, sheds light on how genetic information passes down, uninterrupted, through generations.
The study identified a protein, known as SPOCD1, which plays a key role in protecting the early-stage precursors to sperm, known as germ cells, from damage in a developing embryo.
During their development, germ cells undergo a reprogramming process that leaves them vulnerable to rogue genes, known as jumping genes, which can damage their DNA and lead to infertility.