Archive for the ‘biotech/medical’ category: Page 122
Aug 4, 2024
How do aging brain blood vessels contribute to cognitive decline?
Posted by The Neuro-Network in categories: biotech/medical, life extension, neuroscience
Aging is associated with blood flow changes in the brain.
These changes may be linked to an increased risk of neurodegenerative conditions.
Researchers have mapped the aging processes of blood vessels in the brains of mice in an effort to establish how they affect cognitive decline.
Continue reading “How do aging brain blood vessels contribute to cognitive decline?” »
Aug 4, 2024
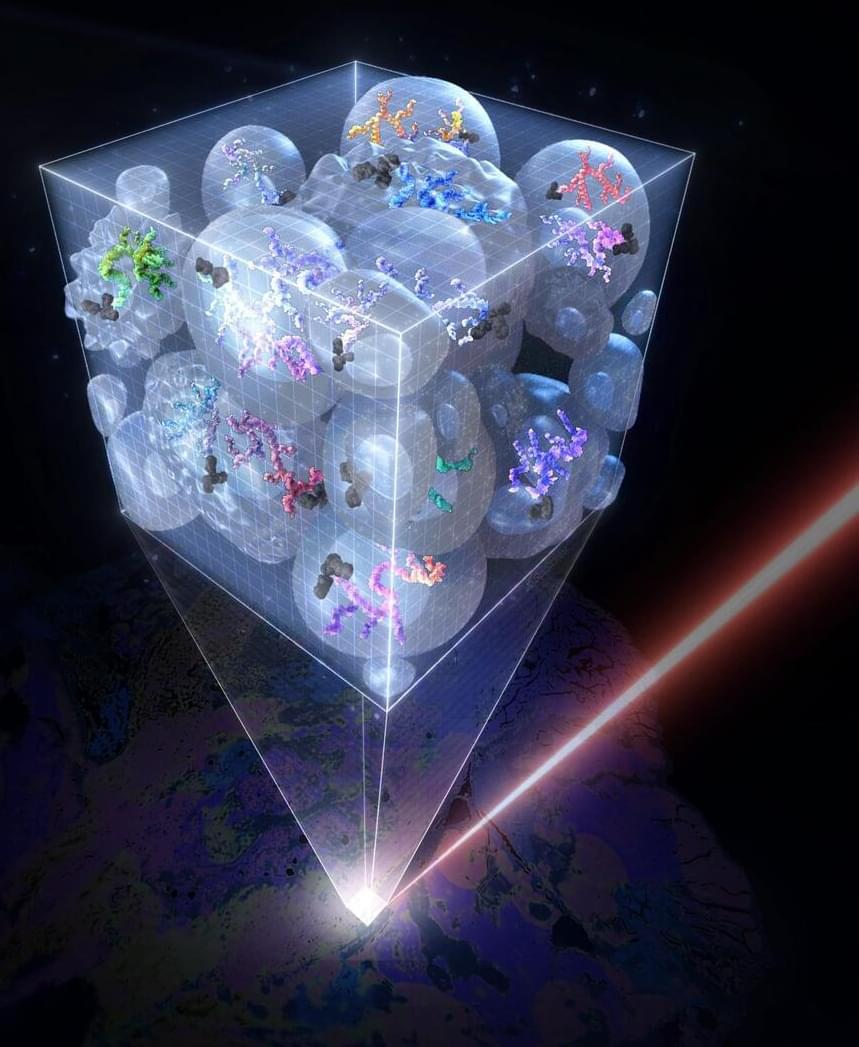
Revolutionary DNA Nanotech Boosts Mass Cytometry by 500-Fold
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: biotech/medical, health, nanotechnology
ACE, a groundbreaking DNA-powered signal amplification technology, significantly enhances the sensitivity of mass cytometry, providing new insights into various biological and pathological processes.
Since the 1950s, researchers have employed “flow cytometry,” a renowned technique devised by Wallace Coulter, to characterize various types of immune cells in research studies and human blood samples. This method has significantly enhanced our understanding of immune cell development and provided innovative approaches for evaluating human health and diagnosing various blood cancers. Eventually, flow cytometry was extended to analyze other cell types as well.
In traditional flow cytometry, cell surface and intracellular proteins are detected with antibody molecules that are linked to fluorescent probes. However, while providing single-cell sensitivity, this method is limited in detecting multiple proteins by the number of fluorophores that can be clearly distinguished within the entire spectrum of fluorescent light.
Aug 4, 2024
Cell-type specific epigenetic clocks to quantify biological age at cell-type resolution
Posted by Shubham Ghosh Roy in categories: biotech/medical, genetics, life extension, neuroscience
 The ability to accurately quantify biological age could help monitor and control healthy aging. Epigenetic clocks have emerged as promising tools for estimating biological age, yet so far, most of these clocks have been developed from heterogeneous bulk tissues, and are thus composites of two aging processes, one reflecting the change of cell-type composition with age and another reflecting the aging of individual cell-types. There is thus a need to dissect and quantify these two components of epigenetic clocks, and to develop epigenetic clocks that can yield biological age estimates at cell-type resolution. Here we demonstrate that in blood and brain, approximately 35% of an epigenetic clock’s accuracy is driven by underlying shifts in lymphocyte and neuronal subsets, respectively. Using brain and liver tissue as prototypes, we build and validate neuron and hepatocyte specific DNA methylation clocks, and demonstrate that these cell-type specific clocks yield improved estimates of chronological age in the corresponding cell and tissue-types. We find that neuron and glia specific clocks display biological age acceleration in Alzheimer’s Disease with the effect being strongest for glia in the temporal lobe. The hepatocyte clock is found accelerated in liver under various pathological conditions. In contrast, non-cell-type specific clocks do not display biological age-acceleration, or only do so more marginally. In summary, this work highlights the importance of dissecting epigenetic clocks and quantifying biological age at cell-type resolution.
The ability to accurately quantify biological age could help monitor and control healthy aging. Epigenetic clocks have emerged as promising tools for estimating biological age, yet so far, most of these clocks have been developed from heterogeneous bulk tissues, and are thus composites of two aging processes, one reflecting the change of cell-type composition with age and another reflecting the aging of individual cell-types. There is thus a need to dissect and quantify these two components of epigenetic clocks, and to develop epigenetic clocks that can yield biological age estimates at cell-type resolution. Here we demonstrate that in blood and brain, approximately 35% of an epigenetic clock’s accuracy is driven by underlying shifts in lymphocyte and neuronal subsets, respectively. Using brain and liver tissue as prototypes, we build and validate neuron and hepatocyte specific DNA methylation clocks, and demonstrate that these cell-type specific clocks yield improved estimates of chronological age in the corresponding cell and tissue-types. We find that neuron and glia specific clocks display biological age acceleration in Alzheimer’s Disease with the effect being strongest for glia in the temporal lobe. The hepatocyte clock is found accelerated in liver under various pathological conditions. In contrast, non-cell-type specific clocks do not display biological age-acceleration, or only do so more marginally. In summary, this work highlights the importance of dissecting epigenetic clocks and quantifying biological age at cell-type resolution.
The authors have declared no competing interest.
The Illumina DNA methylation datasets analyzed here are all freely available from GEO (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo).
Aug 4, 2024
Telomerase gene therapy shows promising potential for treating pulmonary fibrosis
Posted by Paul Battista in categories: biotech/medical, life extension, robotics/AI

Telomerase gene therapy shows promising potential for treating pulmonary fibrosis and other diseases associated with short telomeres.
Aug 4, 2024
Anti-Aging Antibodies?
Posted by Montie Adkins in categories: biotech/medical, education, life extension

There’s only one alliterative phrase i like more than ‘the sheekey science show’, and that’s ‘anti-aging antibodies’. now, as it happens, one thing i spent a lot of time working on this year is antibodies. Antibody, make me feel this way. now while i cannot tell you yet what i was/am doing, i can tell you about two recent science stories that exploit antibodies to extend mouse lifespan. Firstly, i will bring your attention to this paper — immunotherapy targeting isoDGR-protein damage extends lifespan and then we’ll look at this paper that came out last month — Inhibition of IL-11 signalling extends mammalian healthspan.
Find me on Twitter — / eleanorsheekey.
Aug 4, 2024
Lead Is Associated With An Older Biological Age And An Increased Mortality Risk
Posted by Mike Lustgarten in categories: biotech/medical, life extension
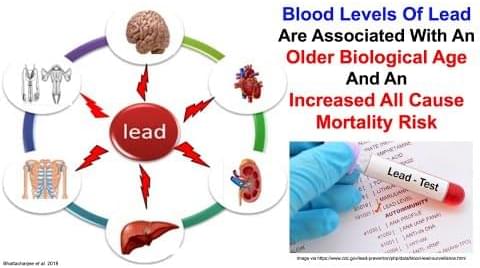
Join us on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhDDiscount Links/Affiliates: Blood testing (where I get my labs): https://www.ultalabtests.com/.…
Aug 3, 2024
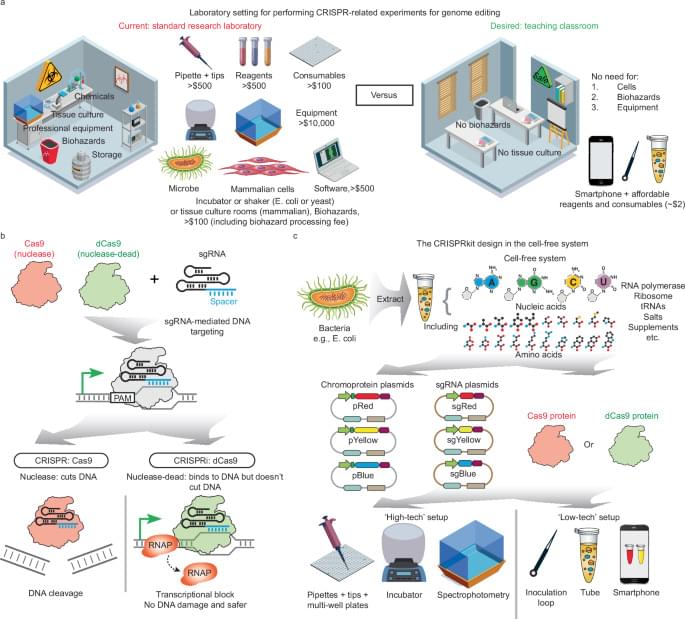
A frugal CRISPR kit for equitable and accessible education in gene editing and synthetic biology
Posted by Paul Battista in categories: bioengineering, biotech/medical, education, information science
Equitable and accessible education in life sciences, bioengineering, and synthetic biology is crucial for training the next generation of scientists. Here the authors present the CRISPRkit, a cost-effective educational tool that enables high school students to perform CRISPR experiments affordably and safely without prior experience, using smartphone-based quantification and an automated algorithm for data analysis.
Aug 2, 2024
The Term “AI” Has Become a Dirty Word in the World of Marketing
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in categories: biotech/medical, health, robotics/AI
It seems that Silicon Valley giants, AAA game developers, and other companies desperately clinging to the AI trend and trying to integrate the technology into any product they own will soon have to rethink their marketing strategies, as a new study conducted by researchers from Washington State University indicates that using terms like “AI” or “artificial intelligence” in product descriptions can negatively impact sales.
To explore the impact of including “AI” in goods and service descriptions on consumers’ purchase intentions, the team conducted six experiments and surveyed over a thousand people, discovering that the use of these terms decreases purchase intention and lowers emotional trust, leading to what any company fears the most – diminishing sales numbers.
Furthermore, the researchers found that putting artificial intelligence in the spotlight can be even more detrimental when it comes to high-risk products – those consumers typically think twice about buying, such as expensive gadgets and medical services – compared to low-risk items, primarily because of the greater likelihood of incurring monetary losses or facing health risks.
Aug 2, 2024
White matter may aid recovery from spinal cord injuries: Study
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in categories: biotech/medical, neuroscience
Injuries, infection and inflammatory diseases that damage the spinal cord can lead to intractable pain and disability. Some degree of recovery may be possible. The question is, how best to stimulate the regrowth and healing of damaged nerves.
At the Vanderbilt University Institute of Imaging Science (VUIIS), scientists are focusing on a previously understudied part of the brain and spinal cord —white matter. Their discoveries could lead to treatments that restore nerve activity through the targeted delivery of electromagnetic stimuli or drugs.
As in the brain, the spinal cord is made up nerve cell bodies (gray matter), which process sensation and control voluntary movement, and axons (white matter), fibers that connect nerve cells and which project to the rest of the body.