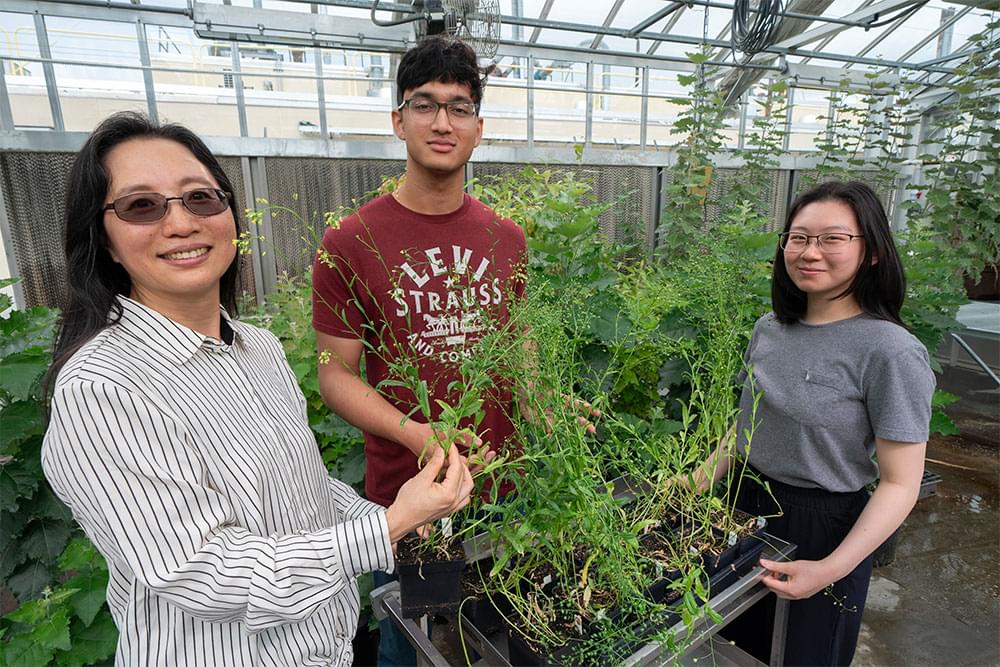
UPTON, N.Y. — Efforts to achieve net-zero carbon emissions from transportation fuels are increasing demand for oil produced by nonfood crops. These plants use sunlight to power the conversion of atmospheric carbon dioxide into oil, which accumulates in seeds. Crop breeders interested in selecting plants that produce a lot of oil look for yellow seeds. In oilseed crops like canola, yellow-seeded varieties generally produce more oil than their brown-seeded counterparts. The reason: The protein responsible for brown seed color — which yellow-seeded plants lack — also plays a key role in oil production.
Now, plant biochemists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory — who are interested in increasing plant oil synthesis for the sustainable production of biofuels and other bioproducts — have harnessed this knowledge to create a new high-yielding oilseed crop variety. In a paper just published in The Plant Biotechnology Journal, they describe how they used tools of modern genetics to produce a yellow-seeded variety of Camelina sativa, a close relative of canola, that accumulates 21.4% more oil than ordinary camelina.
“If breeders can get a few percent increase in oil production, they regard it as significant, because even small increases in yield can lead to large increases in oil production when you’re planting millions of acres,” said Brookhaven Lab biochemist John Shanklin, chair of the Lab’s Biology Department and leader of its plant oil research program. “Our nearly 22% increase was unexpected and could potentially result in a dramatic increase in production,” he said.