Apr 19, 2022
NASA Beamed a Doctor to The ISS in a World-First ‘Holoportation’ Achievement
Posted by Carse Peel in categories: augmented reality, biotech/medical
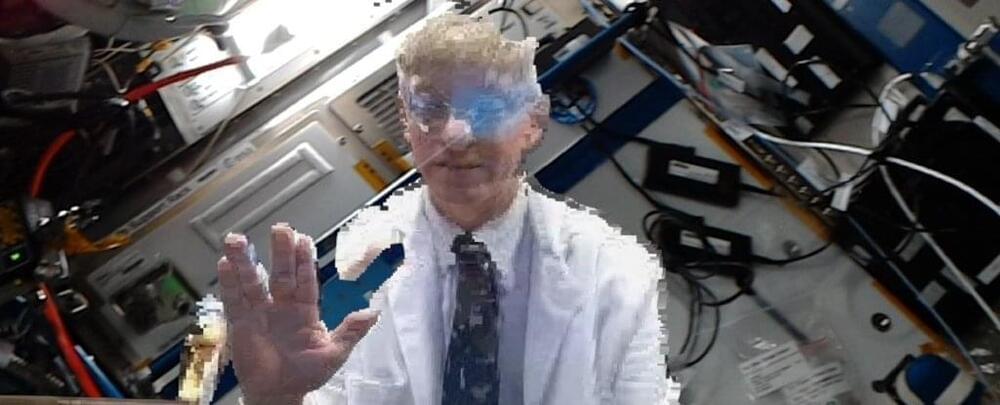
There’s never been a house call quite like this. In a first for telepresence communication, a NASA flight surgeon was ‘holoported’ to the International Space Station (ISS), appearing and conversing as a virtual presence in real time, hundreds of miles above the surface of Earth.
If it sounds like Star Trek, you’re not too far off. (after all, Star Trek: Voyager did feature an artificial physician who was a holographic projection.)
But this isn’t science fiction. When NASA flight surgeon Josef Schmid was beamed up to the ISS in October of last year, the illusion was made possible thanks to Microsoft’s ‘holoportation’ technology, which lets users interact with 3D representations of remote participants in real time.