Feb 18, 2022
The hepatoprotective effects of fennel seeds extract and trans‐Anethole in streptozotocin‐induced liver injury in rats
Posted by Omuterema Akhahenda in categories: biotech/medical, food
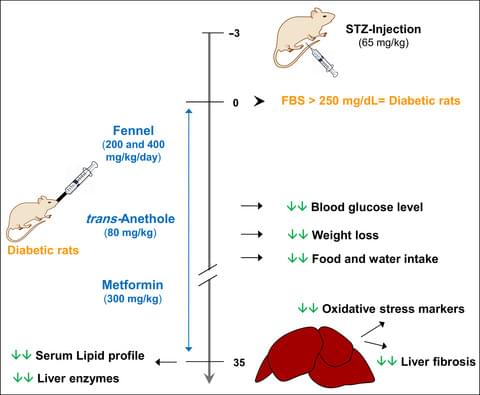
Hypoglycemic, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant activities of fennel have been recorded in numerous investigations. The study aimed to evaluate the protective effects of fennel or its active component trans-Anethole (TA) on streptozotocin-induced liver injury in rats. Rats were injected with a single dose of STZ (65 mg/kg) and treated with fennel (200 and 400 mg/kg), TA (80 mg/kg), or metformin (300 mg/kg) for 35 days. Serum lipid profile and liver enzyme activity (aminotransferases), oxidative stress markers, and the degree of fibrosis in the liver tissue were assessed. Both fennel and TA decreased blood glucose levels, reduced liver enzyme activity, food, and water intake, and intensity of weight loss, reduced serum triglycerides (TG), total cholesterol (TC), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-c), and increased high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-c). Additionally, fennel and TA significantly reduced MDA concentration while increased CAT activity and thiol content and reduced the degree of injury and fibrosis in the liver of diabetic rats. Our results suggest that fennel seed extract and its active compound TA are able to protect the liver against diabetes-induced hepatic injury in rats, probably via hypoglycemic and antioxidant effects.
The effects of fennel seed extract and its active compound trans-Anethole were investigated in the STZ-induced liver injury in rats. Both fennel and trans-Anethole effectively reduced blood glucose l…