Humans have been trying to cheat death for thousands of years. Myths about elixirs promising immortality span various cultures, as do real concoctions that often did more harm than good. One of the most misguided attempts at creating a potion for immortality involved the first emperor of China and mercury pills. In his obsession with finding a formula that would grant him eternal life, Qin Shi Huang downed mercury and other toxic substances nearly two millennia ago, believing his alchemists had hit upon the perfect magical tonic. Unsurprisingly, he died prematurely at age 49.
Archeologists have discovered another 2,000-year-old “elixir for immortality” that sheds light on the true cost of chasing down eternal life.
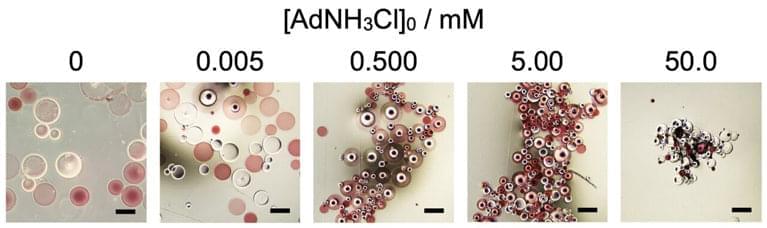
While excavating the tomb of a Western Han noble family in China’s Henan province in 2018, researchers unearthed a bronze pot. At first, the team thought the liquid inside was wine, but more recently determined that it was an alchemist’s formulation: a yellow liquid containing potassium nitrate and alunite. These two ingredients are cited in ancient Taoist texts as ingredients for immortality. Potassium nitrate is an inorganic salt used today as a natural source of nitrate, and is a useful ingredient in food preservatives, fertilizer, and fireworks. Alunite is a mineral that forms in volcanic or sedimentary environments when sulfur-rich minerals oxidize. It has historically been used to make alum, which is important for water purification, tanning, and dyeing.