Woo and other entrepreneurs are using fasts and other tricks to “hack” their brain chemistry like they would a computer, hoping to give themselves an edge as they strive to dream up the next billion-dollar idea. Known by insiders as “biohacking,” the push for cognitive self-improvement is gaining momentum in the Silicon Valley tech world, where workers face constant pressure to innovate and produce at the highest levels.
Category: bioengineering – Page 210
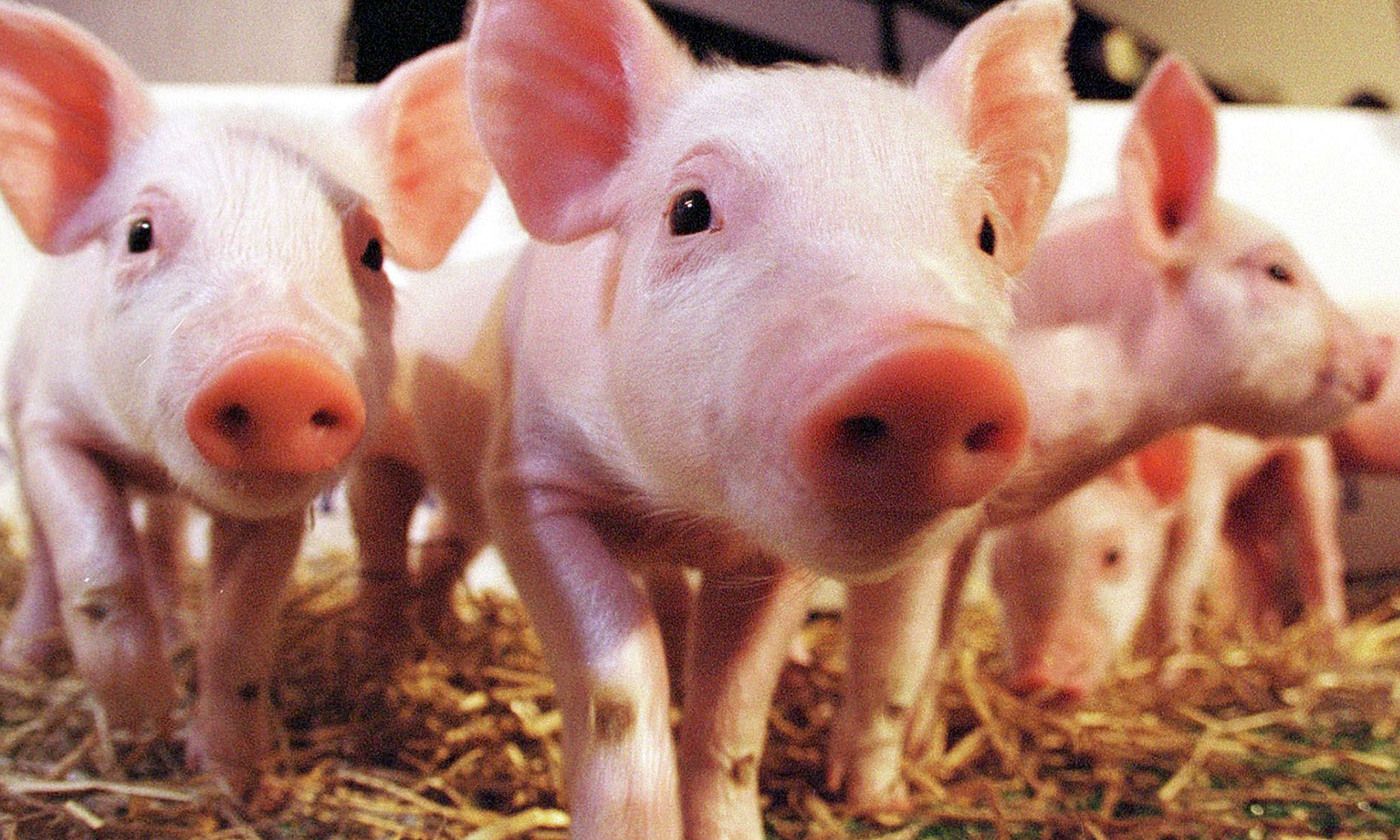
There is a well-documented organ shortage throughout the world. For example, 3,000 kidney transplants were made last year in the United Kingdom, but that still left 5,000 people on the waiting list at the end of the period. A lucrative trade in organs has grown up, and transplant tourism has become relatively common. While politicians wring their hands about sensible solutions to the shortage, including the nudge of opt-out donation, scientists using genetic manipulations have been making significant progress in growing transplantable organs inside pigs.
Scientists in the United States are creating so-called ‘human-pig chimeras’ which will be capable of growing the much-needed organs. These chimeras are animals that combine human and pig characteristics. They are like mules that will provide organs that can be transplanted into humans. A mule is the offspring of a male donkey (jack) and a female horse (mare). Horses and donkeys are different species with different numbers of chromosomes, but they can breed together.
In this case, the scientists take a skin cell from a human and from this make stem cells capable of producing any cell or tissue in the body, known as ‘induced pluripotent stem cells’. They then inject these into a pig embryo to make a human-pig chimera. In order to create the desired organ, they use gene editing, or CRISPR, to knock out the embryo’s pig’s genes that produce, for example, the pancreas. The human stem cells for the pancreas then make an almost entirely human pancreas in the resulting human-pig chimera, with just the blood vessels remaining porcine. Using this controversial technology, a human skin cell, pre-treated and injected into a genetically edited pig embryo, could grow a new liver, heart, pancreas or lung as required.
Transhuman Terminology.
ADHOCRACY
AEONOMICS
A-LIFE
AGORIC SYSTEM
AI-COMPLETE ALEPH ALGERNON AMORTALIST ARACHNIOGRAPHY ARCH-ANARCHY ARCOLOGY ARROW IMPOSSIBILITY THEOREM ARTILECT ASEX ASIMORT ASIMOV ASSEMBLER ATHANASIA ATHANOPHY ATHEOSIS AUGMENT AUTOEVOLUTIONIST AUTOMATED ENGINEERING AUTOMORPHISM AUTOPOTENT AUTOSCIENT BABY UNIVERSE BASEMENT UNIVERSE BEAN DIP CATASTROPHE BEANSTALK BEKENSTEIN BOUND BERSERKER BETELGEUSE-BRAIN BIG CRUNCH BINERATOR BIOCHAUVINISM BIOLOGICAL FUNDAMENTALISM BIONICS BIONOMICS BIOPHILIAC BIOSTASIS B-LIFE BLIGHT BLIND UPLOADING BLUE GOO BOGOSITY FILTER BORGANISM BREAKEVEN POINT BROADCATCHING BRUTE FORCE UPLOADING BUSH ROBOT CALCUTTA SYNDROME CALM TECHNOLOGY CALORIE RESTRICTION CASIMIR EFFECT CEREBROSTHESIS CHINESE ROOM CHRONONAUTS CHURCH-TURING THESIS COBOTS COMPUFORM COMPUTRONIUM CONCENTRATED INTELLIGENCE CONSILIENCE CONNECTIONISM CONTELLIGENCE CONTINUITY IDENTITY THEORY COSMYTHOLOGY CRYOBIOLOGY CRYOCRASTINATE CRYOGENICS CRYONICS CRYONIC SUSPENSION CRYPTO ANARCHY CRYPTOCOSMOLOGY CYBERCIDE CYBERFICTION CYBERGNOSTICISM CYBERIAN CYBERNATE/CYBERNIZE CYBERSPACE/CYBERMATRIX CYBRARIAN CYPHERPUNK DEANIMALIZE DEATH FORWARD DEATHISM DEEP ANARCHY DEFLESH DIGITAL PSEUDONYM DIAMONDOID DISASSEMBLER DISASTERBATION DISTRIBUTED INTELLIGENCE DIVERGENT TRACK HYPOTHESIS DIVERSITY IQ DIVIDUALS DOOMSDAY ARGUMENT DOWNLOAD DRYWARE DUBIFIER DYSON SPHERE ECOCALYPSE ECTOGENESIS
EMBRYOMEME
EMULATION
ENHANCED REALITY
ENVIROCAPITALISM
EPHEMERALISTS
E-PRIME
ESCALATORLOGY
THE ETERNAL LIFE POSTULATE
EUPSYCHIA
EUTHENICS
EVOLUTIONARILY STABLE STRATEGY (ESS)
EVOLUTURE
EXCONOMICS
EXES
EXFORMATION
EXISTENTIAL TECHNOLOGY
EXOPHOBIA
EXOSELF
EXTROPIAN
EXTROPIATE
EXTROPIC
EXTROPOLIS
EXTROPY
FACULTATIVE ANAGOROBE
FAR EDGE PARTY
THE FERMI PARADOX
FEMTOTECHNOLOGY
FLATLANDER
FLUIDENTITY
FOGLET
FORK
FREDKIN’S PARADOX
FUNCTIONAL SOUP
FUTIQUE
FUTURE SHOCK
GALAXY BRAIN
GAUSSIAN
GENEGENEERING
GENETIC ALGORITHM
GENIE
GREEN GOO
GÖDEL’S THEOREM
GOLDEN GOO
GREAT FILTER, THE
GREY GOO
GUY FAWKES SCENARIO
HALLUCINOMEMIC
HIVE COMPUTING
HOMORPH
HPLD
HYPERTEXT
HYPONEIRIA
HYPOTECH
IDEAL IDENTITY
IMMORTALIST
IMMORTECHNICS
IMP
INACTIVATE
INFOGLUT
INFOMORPH
INFORMATION-THEORETICAL DEATH
INLINE UNIVERSITIES
INTERFACER
INTERNALNET
JUPITER-BRAIN
KHAKI GOO
KARDASCHEV TYPES
KNOWBOTS
KOLMOGOROV COMPELXITY
LEONARDO DA VINCI SYNDROME
LINDE SCENARIO
LIQUIDENTITY
LOFSTROM LOOP
LONGEVIST
MASPAR
MATAGLAP
MEGATECHNOLOGY (or MEGASCALE ENGINEERING)
MEMETICS
MEMIE
MEMIUS
MEMOTYPE
MEMOID (or MEMEOID)
MEHUM
MERCHANCY
MESOSCALE
MINDKIND
MOLMAC
MORPHOLOGICAL FREEDOM
MUTUAL REALITY
NANARCHIST
NANARCHY
NANITE
NANOCHONDRIA
NANOFACTURE
NANOMEDICINE
NANOSOME
NANOTECH
(MOLECULAR) NANOTECHNOLOGY
NEG
NEOMORPH
NEOLOGOMANIA
NEOPHILE
NEOPHILIA
NEOPHOBE
NEUROCOMPUTATION
NEURONAUT
NEURON STAR
NEUROPROSTHESIS
NEUROSUSPENSION
NOOTROPIC
NOW SHOCK
NUTRACEUTICAL
OFFLOADING
OMEGA POINT
OMEGON
OMNESCIENCE
O’NEILL COLONY
O’NEILL CYLINDERS
ONTOLOGICAL CONSERVATIVES
OPTIMAL PERSONA
PANCRITICAL RATIONALISM
ORBITAL TOWER
PARTIALATE
PATTERN IDENTITY THEORY
PERICOMPUTER
PERIMELASMA
PERSOGATE
PERVERSION ATTACK
PHARMING
PHYLE
PHYSICAL ESCHATOLOGY
PICO TECHNOLOGY
PIDGIN BRAIN
PINK GOO
PLEXURE
POME
POSTHUMAN
POSTJUDICE
POWERSHIFT
PRISONERS’ DILEMMA
PRIVACY MANAGEMENT
PROLONGEVITY
QUANTUM COMPUTING
QUANTUM CRYPTOGRAPHY
QUASISPECIES
RAPTURE OF THE FUTURE
RED GOO
RED QUEEN PRINCIPLE
RED QUEENED
REMEMBRANCE AGENT
REVERSIBLE
RIF
SANS CEILING HYPOTHESIS
SANTA MACHINE
SAPPER MEME
SCHEME
SENTIENCE QUOTIENT
SHIH
SINGULARITY
SINGULARITARIAN
SKY HOOK
SMART-FACED
SOCIOTYPE
SOLID STATE CIVILIZATION
SPIKE, THE
SPOCK MEME
SPONTANEOUS VOLUNTARISM
SPACE FOUNTAIN
STAR LIFTING
STELLAR HUSBANDRY
STEWARD
STRONG AI POSTULATE
STRONG CONVERGENCE HYPOTHESIS
SUSPENDED ANIMATION
SYNTHESPIAN
TAZ/Temporary Autonomous Zone.
TECHNOCYTE
TECHNOSPHERE
TECHNOCALYPS
TELEOLOGICAL THREAD
THEORETICAL APPLIED SCIENCE
TITHONUS SYNDROME
TIPLER CYLINDER
TIPLERITE
TRANSBIOMORPHOSIS (TRANSBIOLOGICAL METAMORPHOSIS)
TRANSCEND
TRANSCENSION
TRANSCIENT
TRANSCLUSION
TRANSHUMANISM
TRANSHUMANITIES
TRAPDOOR FUNCTION
TURING MACHINE
TURING TEST
ÜBERGOO
UBIQUITOUS COMPUTING
UPLIFT
UPLOADER
UNIVERSAL CONSTRUCTOR
UNIVERSAL IMMORTALISM
UNIVERSAL TURING MACHINE
UTILITY FOG
VACCIME
VASTEN
VENTURISM
VIEWQUAKE
VIRIAN
VIRION
VIRTUAL COMMUNITY
VIRTUAL RIGHTS
VITOLOGY
VIVISYSTEM
VON NEUMANN MACHINE
VON NEUMANN PROBE
WEBORIZE
WETWARE
WORMHOLE
XENOBIOLOGY
XENOEVOLUTURE
XEROPHILIA
XOXER
ZERO KNOWLEDGE PROOF
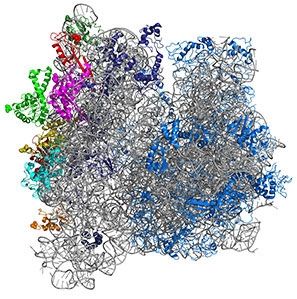
Over the past several years, Northwestern Engineering’s Michael Jewett did the seemingly impossible. He overcame the critical barrier to making mutant ribosomes, the core catalyst in cells that are responsible for life.
Now, with funding from the Department of Defense’s Multidisciplinary University Research Initiatives (MURI) program, Jewett is ready to take this research to the next level. Along with a multi-school team, he plans to use engineer and repurpose the ribosome to make new kinds of polymers for flow batteries.
“We are in a new era of biomaterial design,” Jewett said. “So far, the ribosome has been this untouchable biomolecular machine — one that we couldn’t engineer or modify. Now, armed with recent advances in our ability to construct new versions, new applications may only be limited by our imagination.”
The MURI grant joins researchers from Northwestern, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, University of Texas at Austin, and Georgia Institute of Technology who will work together to develop new types of electrical materials for battery storage. By using biological catalysts, the team aims to produce materials for sustainable, rechargeable batteries that are currently impossible to make chemically.
ANN ARBOR, Mich., –July 12, 2016- Kraig Biocraft Laboratories, Inc. (OTCQB: KBLB) (“Company”), the leading developer of spider silk based fibers, today announced that it has received a contract valued at up to $1.0 million, if the option phase is awarded, for the development of high performance fibers for protective apparel applications. Under the fully funded base effort, valued at $99,962, the Company will deliver ballistic shoot packs constructed from its proprietary Dragon Silk™ material for performance testing. These shoot packs will be tested and evaluated for critical Soldier protective applications including ballistic impact. If awarded, the option phase will significantly expand this work with the US Army.
“Dragon Silk scores very highly in tensile strength and elasticity, which makes it one of the toughest fibers known to man and the ideal material for many applications,” stated Jon Rice, COO. “Providing material for this ballistic shoot pack initiative is an important next step for Kraig and spider silk. This contract reinforces the many significant potential applications for recombinant spider silk. Today is a great day for spider silk.”
“We’re proud to be working with the Department of Defense to assess the exciting potential of spider silk for military applications,” stated Kim K Thompson, CEO and founder of Kraig Biocraft Laboratories. “We are honored that the U.S. Army has selected us for this program. This effort will provide Kraig Labs with the opportunity to validate our longstanding belief that spider silk technology has had an incredible potential for protective and lifesaving materials and expand our ability to design and engineer innovative materials solutions.”
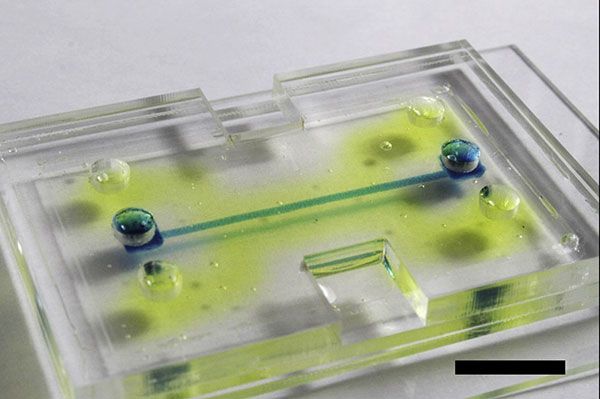
At the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB) and Tufts University a team has developed a microfluidic chip that mimics human tissue for use in drug testing applications. The chip is based on a silk gel that overcomes the limitations of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), a silicon material widely used to host living cells within microfluidic devices. As an example, PDMS has problems handling lipids, absorbing them instead of letting them move freely along with other nearby compounds and so not applicable with lipid-based compounds. Additionally, PDMS is not biodegradable and so a small device based on it can’t easily be used as an implantable. Silk, on the other hand, just needed a bit of engineering to make a candidate that overcomes many of PDMS’s limitations.
From Plough to Pipette
Posted in bioengineering, biological, food
In part 2 of our plant synthetic biology series we teamed up with Cameron Tout of the Legume Laboratory blog to introduce some of the tools of plant synbio and how these are being applied to agriculture.
Over 9000 years ago the first domesticated varieties of wheat were created in South West Asia. What was remarkable about these plants is that they were selected by humans to retain their seeds rather than dispersing them by wind. This meant that wheat became dependent on farmers for propagation, but allowed people to harvest grain without the pods shattering in their hands.
Since then, humans have been modifying plants in ever more sophisticated ways, the 20th century saw the introduction of mutation breeding and hybrid technology, resulting in massive gains in crop yields.