Nov 15, 2023
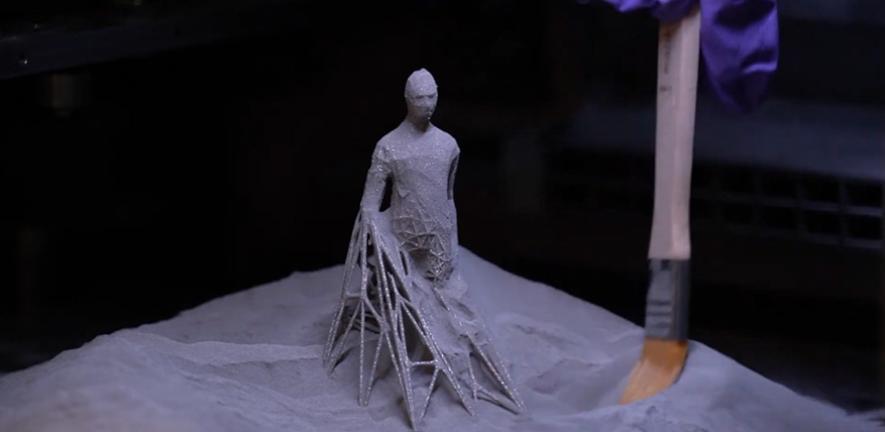
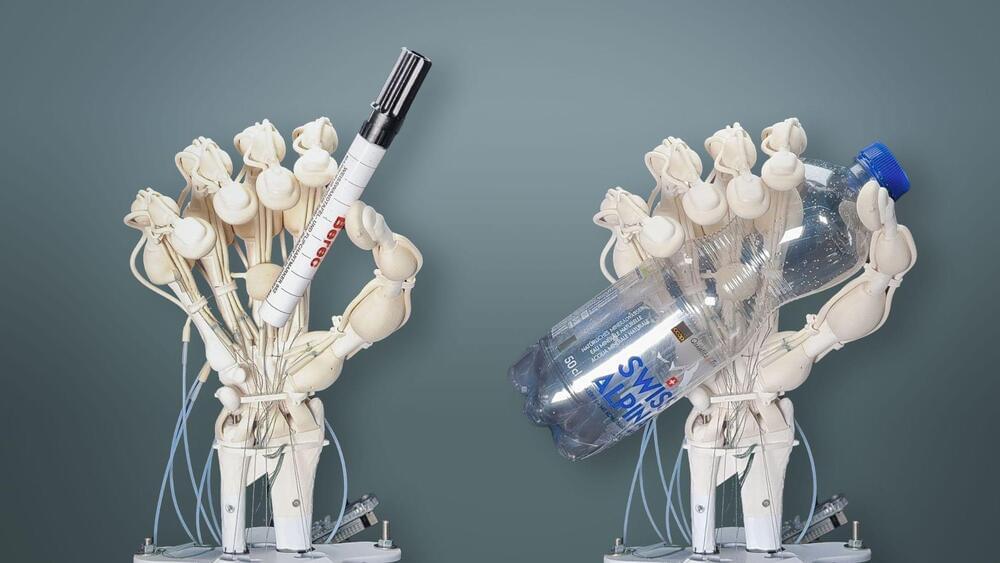
New 3D printing technology enables more durable and flexible robots
Posted by Gemechu Taye in categories: 3D printing, robotics/AI
This opens up new possibilities for creating complex robots with soft and rigid materials in one go.
Thomas Buchner / ETH Zurich.
3D printing is a revolutionary technology that can create objects of any shape and size from various materials. However, until now, it was mostly limited to using fast-curing plastics, which have some drawbacks. They are brittle, prone to cracking, and lose their shape easily when bent.
Continue reading “New 3D printing technology enables more durable and flexible robots” »