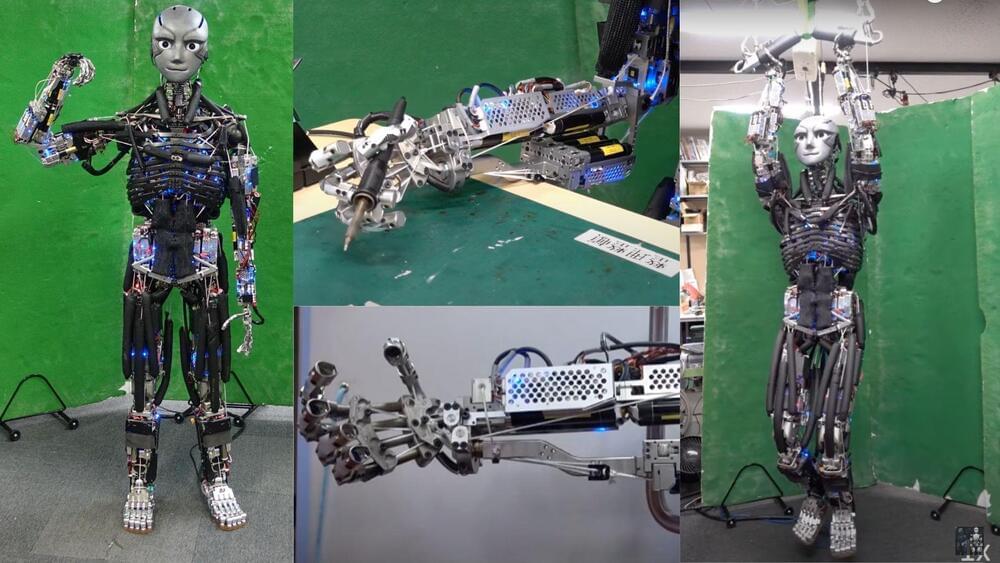
Robotic forearm designed with human-like proportions and efficient heat dissipation:
To replicate this in robots, researchers developed a compact forearm with a radioulnar joint using miniature bone–muscle modules. The design mimics human proportions, with two modules in the radius and ulna, totaling eight muscles. These muscles control six degrees of freedom (DOFs), including the radioulnar joint, radiocarpal joint, and finger movements.
The module’s compact design maintains the correct body proportions and weight ratios while offering more muscle-driven freedom than other robots. The researchers successfully created a forearm that closely mirrors human joint performance, allowing for precise, skillful movements similar to those of a human.
Researchers tested Kengoro, a robot equipped with a human-mimetic radioulnar forearm, by performing tasks like soldering, opening a book, turning a screw, and swinging a badminton racket.









Leave a reply