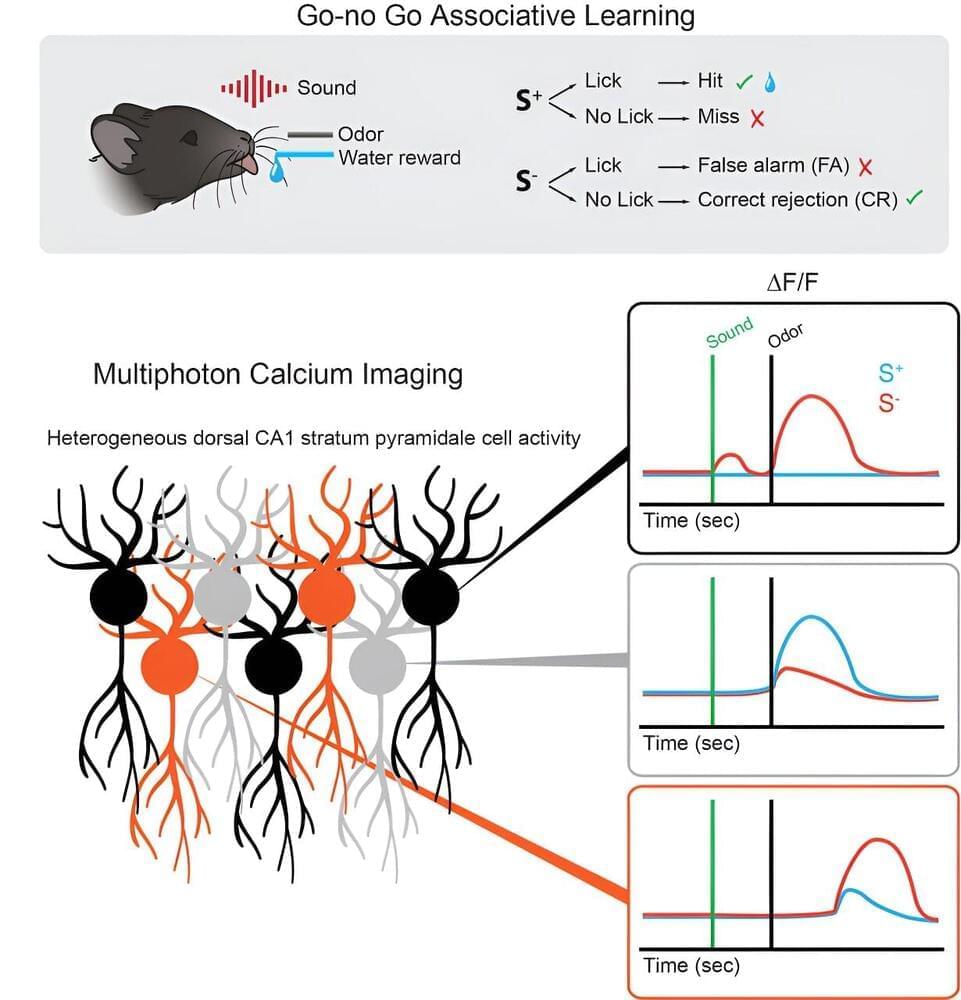
Researchers at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus have discovered that odors stimulate specific brain cells that may play a role in rapid “go/no-go” decision-making.
The study was published online Tuesday (Feb. 6) in the journal Current Biology.
The scientists focused on the hippocampus, an area of the brain crucial to memory and learning. They knew that so-called “time cells” played a major role in hippocampal function, but didn’t know their role in associative learning.








Comments are closed.