How can Marvel movie character Ant-Man produce such strong energy out of his small body? The secret lies in the transistors on his suit that amplify weak signals for processing. Transistors that amplify electrical signals in the conventional way lose heat energy and limit the speed of signal transfer, which degrades performance. What if it were possible to overcome such limitations and make a high-performance suit that is light and small but without the loss of heat energy?
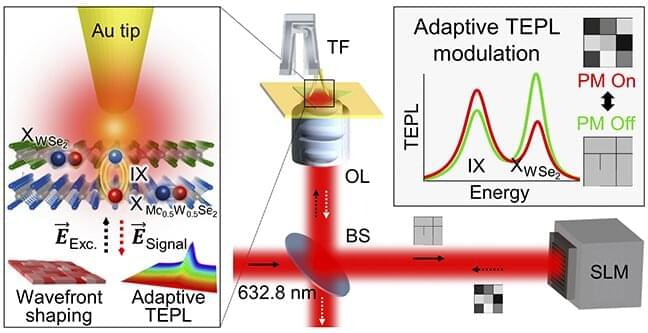
A POSTECH team of Professor Kyoung-Duck Park and Yeonjeong Koo from the Department of Physics and a team from ITMO University in Russia led by Professor Vasily Kravtsov jointly developed a nano-excitonic transistor using intralayer and interlayer excitons in heterostructure-based semiconductors, which addresses the limitations of existing transistors. The research was recently published in the journal ACS Nano.
Excitons are responsible for light emission of semiconductor materials and are key to developing a next-generation light-emitting element with less heat generation and a light source for quantum information technology due to the free conversion between light and material in their electrically neutral states.








Comments are closed.