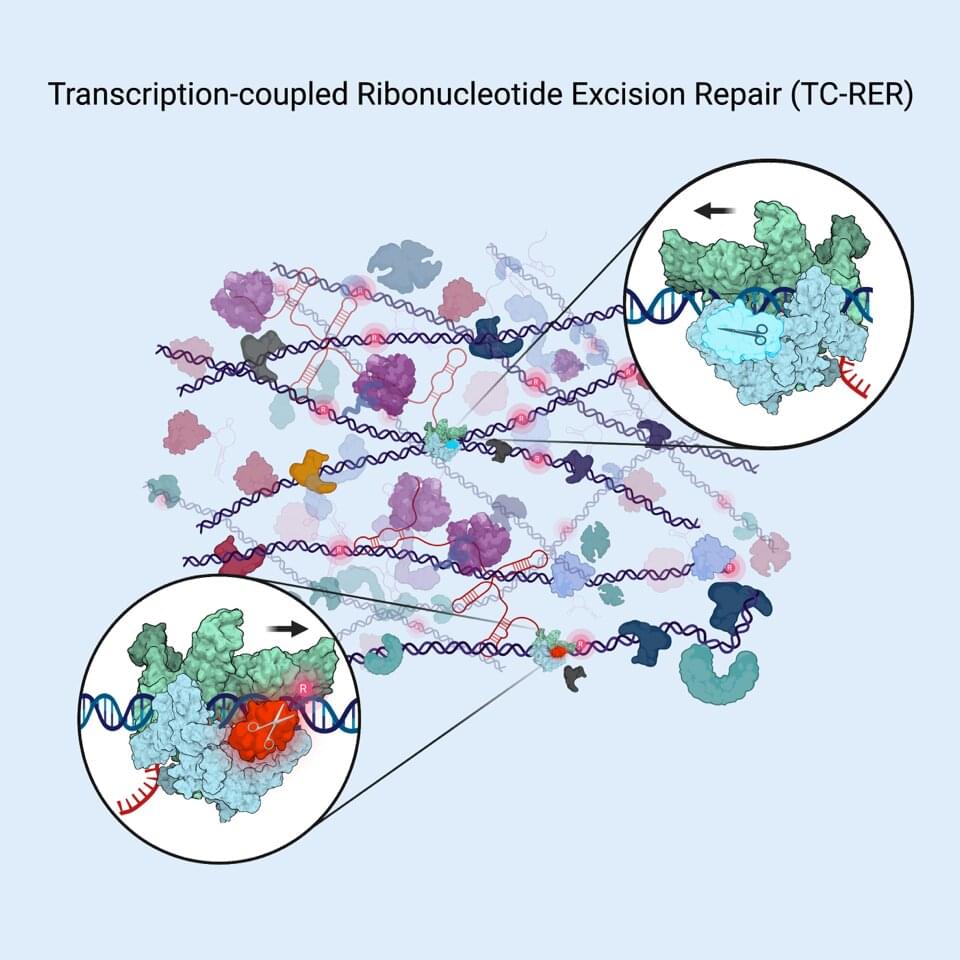
A new study adds to an emerging, radically new picture of how bacterial cells continually repair faulty sections of their DNA.
Published online May 16 in the journal Cell, the report describes the molecular mechanism behind a DNA repair pathway that counters the mistaken inclusion of a certain type of molecular building block, ribonucleotides, into genetic codes. Such mistakes are frequent in code-copying process in bacteria and other organisms. Given that ribonucleotide misincorporation can result in detrimental DNA code changes (mutations) and DNA breaks, all organisms have evolved to have a DNA repair pathway called ribonucleotide excision repair (RER) that quickly fixes such errors.
Last year a team led by Evgeny Nudler, Ph.D., the Julie Wilson Anderson Professor in the Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Pharmacology at NYU Langone Health, published two analyses of DNA repair in living E. coli cells. They found that most of the repair of certain types of DNA damage (bulky lesions), such as those caused by UV irradiation, can occur because damaged code sections have first been identified by a protein machine called RNA polymerase. RNA polymerase motors down the DNA chain, reading the code of DNA “letters” as it transcribes instructions into RNA molecules, which then direct protein building.