😗😁
Scientists in Finland have developed a nanodevice that can measure the absolute power of microwave radiation down to the femtowatt level at ultra-low temperatures—a scale trillion times lower than routinely used in verifiable power measurements. The device has the potential to significantly advance microwave measurements in quantum technology.
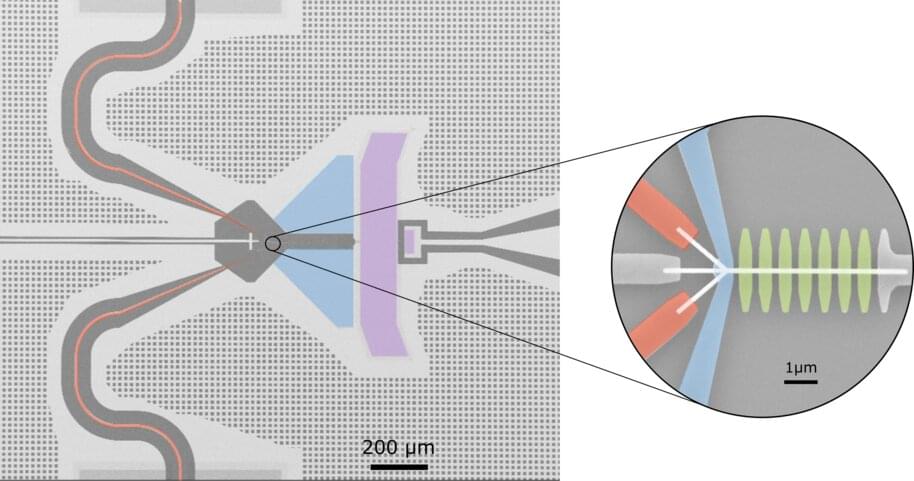
Quantum science takes place mostly at ultra-low temperatures using devices called dilution refrigerators. The experiments also have to be done at tiny energy levels—down to the energy level of single photons or even less. Researchers have to measure these extremely low energy levels as accurately as possible, which means also accounting for heat—a persistent problem for quantum devices.
To measure heat in quantum experiments, scientists use a special type of thermometer called a bolometer. An exceptionally accurate bolometer was recently developed at Aalto University by a team led by Mikko Möttönen, associate professor of quantum technology at Aalto and VTT, but the device had more uncertainty than they had hoped for. Although it enabled them to observe the relative power level, they couldn’t determine the absolute amount of energy very accurately.








Comments are closed.