National University of Singapore (NUS) pharmaceutical scientists have developed synthetic peptide nanonets for treating infections by bacteria strains resistant to last-resort antibiotics.
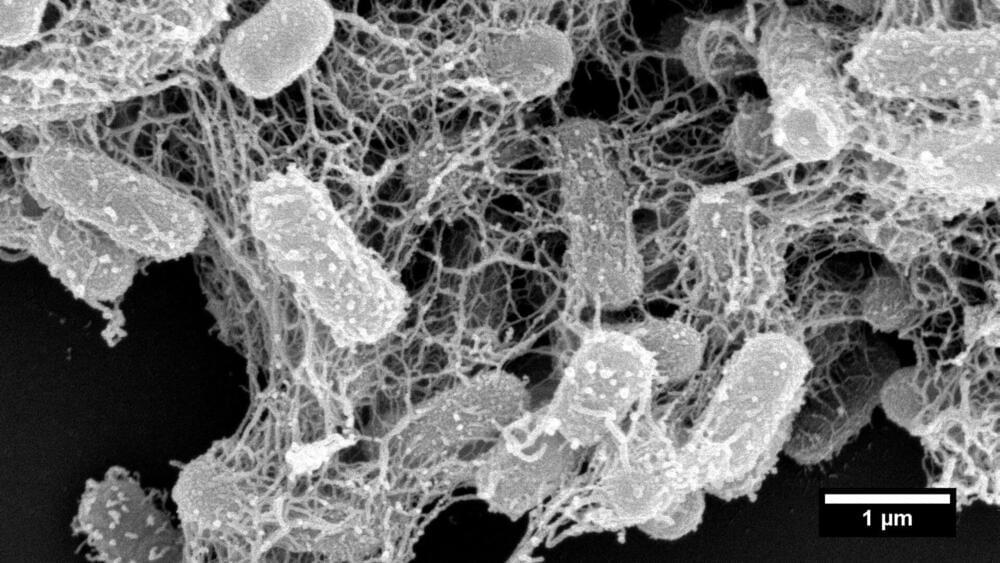
In nature, trap-and-kill is a common immune defense mechanism employed by various species, including humans. In response to the presence of pathogens, peptides are released from host cells and they promptly self-assemble in solution to form cross-linked nanonets, which then entrap the bacteria and render them more vulnerable to antimicrobial components.
Several research groups have explored synthetic biomimetics of nanonets as an avenue for addressing the global healthcare challenge of widespread antibiotic resistance. However, most prominent studies in the field only yielded disjointed short nanofibrils restricted to the bacterial surfaces and are incapable of physically immobilizing the bacteria. Additionally, these designs were lacking in control over the initiation of the self-assembly process.








Comments are closed.