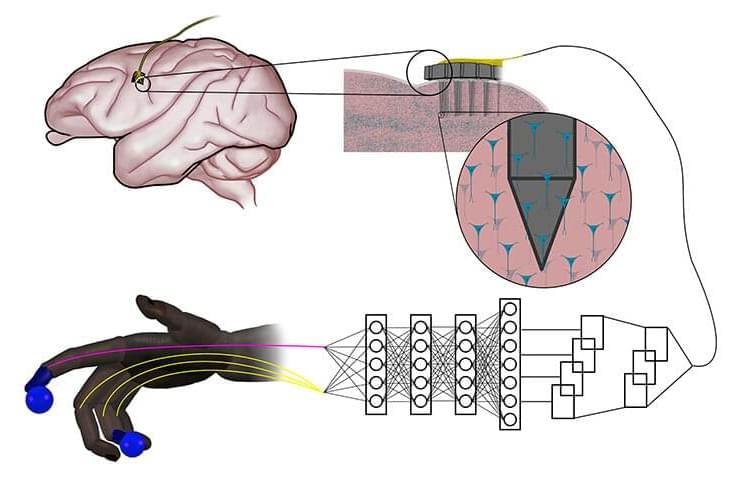
Artificial neural networks that are inspired by natural nerve circuits in the human body give primates faster, more accurate control of brain-controlled prosthetic hands and fingers, researchers at the University of Michigan have shown. The finding could lead to more natural control over advanced prostheses for those dealing with the loss of a limb or paralysis.
The team of engineers and doctors found that a feed-forward neural network improved peak finger velocity by 45% during control of robotic fingers when compared to traditional algorithms not using neural networks. This overturned an assumption that more complex neural networks, like those used in other fields of machine learning, would be needed to achieve this level of performance improvement.
“This feed-forward network represents an older, simpler architecture—with information moving only in one direction, from input to output,” said Cindy Chestek, Ph.D., an associate professor of biomedical engineering at U-M and corresponding author of the paper in Nature Communications.









Comments are closed.