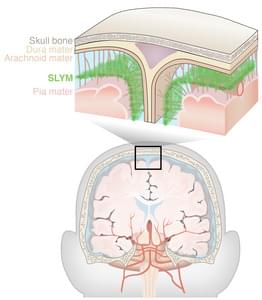
From the complexity of neural networks to basic biological functions and structures, the human brain only reluctantly reveals its secrets. Advances in neuro-imaging and molecular biology have only recently enabled scientists to study the living brain at level of detail not previously achievable, unlocking many of its mysteries. The latest discovery, described today in the journal Science, is a previously unknown component of brain anatomy that acts as both a protective barrier and platform from which immune cells monitor the brain for infection and inflammation.
The new study comes from the labs of Maiken Nedergaard, co-director of the Center for Translational Neuromedicine at University of Rochester and the University of Copenhagen and Kjeld Møllgård, M.D., a professor of neuroanatomy at the University of Copenhagen. Nedergaard and her colleagues have transformed our understanding of the fundamental mechanics of the human brain and made significant findings to the field of neuroscience, including detailing the many critical functions of previously overlooked cells in the brain called glia and the brain’s unique process of waste removal, which the lab named the glymphatic system.
“The discovery of a new anatomic structure that segregates and helps control the flow of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in and around the brain now provides us much greater appreciation of the sophisticated role that CSF plays not only in transporting and removing waste from the brain, but also in supporting its immune defenses,” said Nedergaard.








Comments are closed.