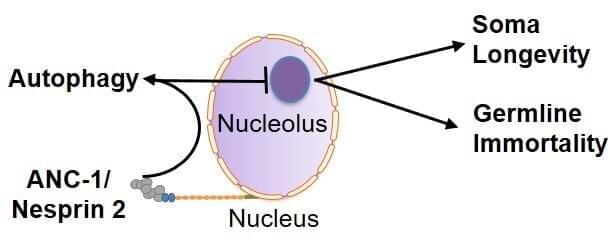
Research at the Institute of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology (IMBB) of the Foundation for Research and Technology-Hellas (FORTH), published today in the journal Nature Aging, reveals a fundamental quality control mechanism that operates in cells to safeguard the integrity and function of the nucleus. By maintaining nuclear homeostasis, this molecular mechanism contributes critically to promote longevity and fertility.
IMBB researchers Dr. Margarita-Elena Papandreou and Dr. Georgios Konstantinidis, headed by Dr. Nektarios Tavernarakis (Professor at the Medical School, University of Crete, and Chairman of the Board at FORTH), discovered that recycling of nuclear and nucleolar components via autophagy delays aging of somatic cells, and sustains the immortality of germ cells, which are required for reproduction.
The nucleus is the central organelle of all eukaryotic cells that contains the genetic material (DNA), which determines cellular identity and function. During aging and in cancer cells, the ultrastructure of the nucleus is dramatically altered. Moreover, progressive and pronounced deterioration of the nuclear architecture is a common and conserved feature of progeria and numerous other disorders associated with aging.









Comments are closed.