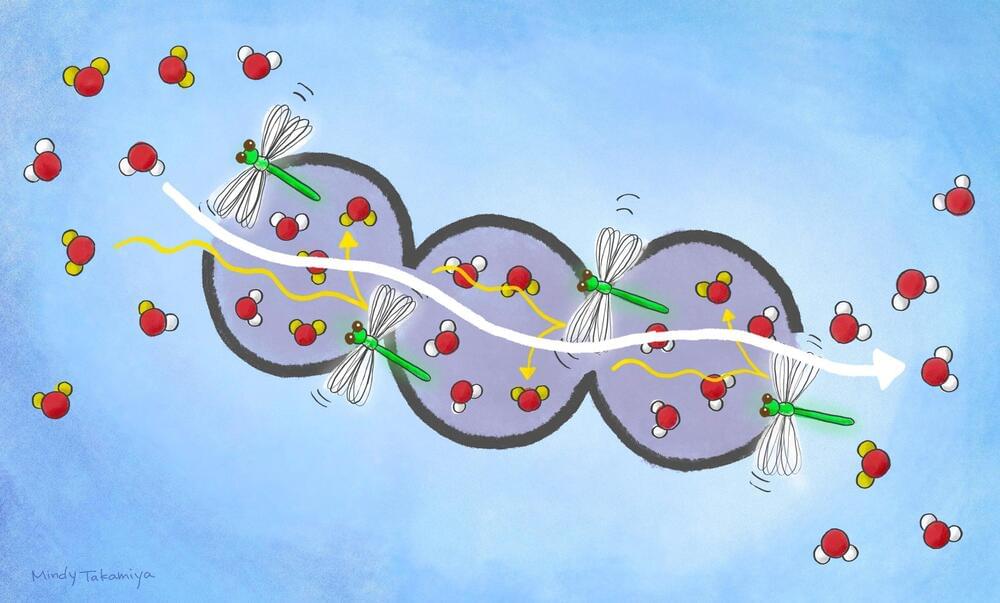
A flipping action in a porous material facilitates the passage of normal water to separate it out from heavy water.
A research group led by Susumu Kitagawa of Kyoto University’s Institute for Cell-Material Sciences (iCeMS), Japan and Cheng Gu of South China University of Technology, China have made a material that can effectively separate heavy water from normal water at room temperature. Until now, this process has been very difficult and energy intensive. The findings have implications for industrial – and even biological – processes that involve using different forms of the same molecule. The scientists reported their results in the journal Nature.
Isotopologues are molecules that have the same chemical formula and whose atoms bond in similar arrangements, but at least one of their atoms has a different number of neutrons than the parent molecule. For example, a water molecule (H2O) is formed of one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms. The nucleus of each of the hydrogen atoms contains one proton and no neutrons. In heavy water (D2O), on the other hand, the deuterium (D) atoms are hydrogen isotopes with nuclei containing one proton and one neutron. Heavy water has applications in nuclear reactors, medical imaging, and in biological investigations.









Comments are closed.