Humanity has come a long way in understanding the universe. We’ve got a physical framework that mostly matches our observations, and new technologies have allowed us to analyze the Big Bang and take photos of black holes. But the hypothetical EmDrive rocket engine threatened to upend what we knew about physics… if it worked. After the latest round of testing, we can say with a high degree of certainty that it doesn’t.
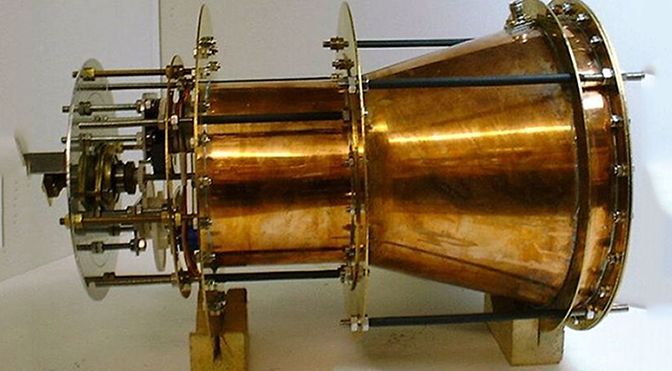
If you have memories from the 90s, you probably remember the interest in cold fusion, a supposed chemical process that could produce energy from fusion at room temperature instead of millions of degrees (pick your favorite scale, the numbers are all huge). The EmDrive is basically cold fusion for the 21st century. First proposed in 2001, the EmDrive uses an asymmetrical resonator cavity inside which electromagnetic energy can bounce around. There’s no exhaust, but proponents claim the EmDrive generates thrust.
The idea behind the EmDrive is that the tapered shape of the cavity would reflect radiation in such a way that there was a larger net force exerted on the resonator at one end. Thus, an object could use this “engine” for hyper-efficient propulsion. That would be a direct violation of the conservation of momentum. Interest in the EmDrive was scattered until 2016 when NASA’s Eagelworks lab built a prototype and tested it. According to the team, they detected a small but measurable net force, and that got people interested.








Comments are closed.