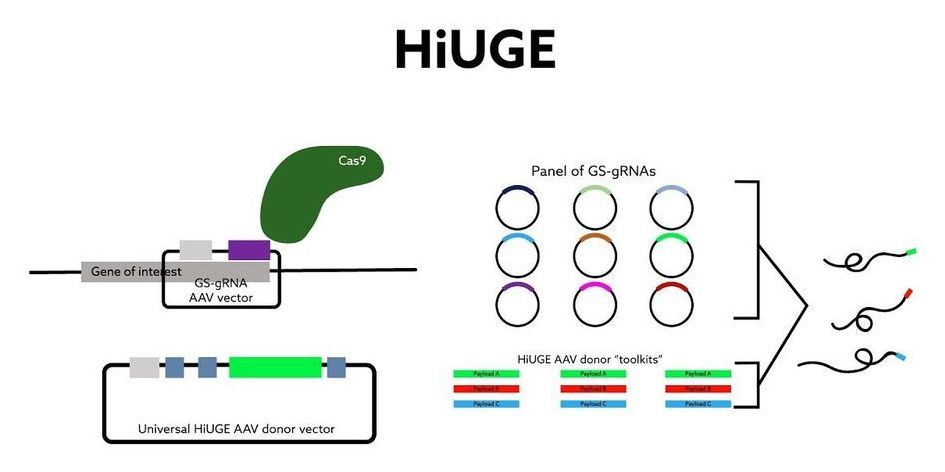
A team of researchers at Duke University have developed an imaging technology for tagging structures at a cellular level that overcomes the shortcomings of existing antibody-based techniques. Immunofluorescence imaging is a key part of the cell biologist’s toolbox, in which a fluorescent ‘flare’ attached to an antibody allows them to visualize the presence of specific target proteins in cell or tissue samples. The issue is that this specificity isn’t always 100 percent — sometimes the antibodies bind to other closely related proteins as well, making it difficult to interpret the results.
Duke’s cell biology chair Scott Soderling has led a team that developed Homology-independent Universal Genome Engineering (HiUGE), an innovation that uses gene-editing technology to rise above the shortcomings of traditional commercial antibodies for imaging.
“We had this idea that CRISPR could be a really amazing tool to address the pressing problem of trying to identify and label these hundreds of proteins,” said Soderling.








Comments are closed.