A team of researchers with members from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Wright-Patterson Air Force Base and the Barnes Group Advisors found that controlling spatter during laser-powder bed fusion can reduce defects in metal-based 3D printing. In their paper published in the journal Science, the group describes studying the additive manufacturing printing methodology and what they learned about it. Andrew Polonsky and Tresa Pollock with the University of California, Santa Barbara have published a Perspective piece on the work done by the team in the same journal issue.
As additive manufacturing printing methodologies mature, new materials are being tested to find out if they might be used in 3D printers to create new products. In recent years, this has extended to metals. One such technique is called laser-powder bed fusion (L-PBF). It involves the use of a high-powered laser to melt and fuse metallic powders layer by layer to produce a 3D part. It has been hoped that the technique could eventually be used for aerospace and biomedical applications. But thus far, such efforts have fallen short due to the large number of defects that occur with the process. In this new effort, the researchers have discovered a way to reduce such defects, perhaps paving the way for the technique to finally fulfill its promise.
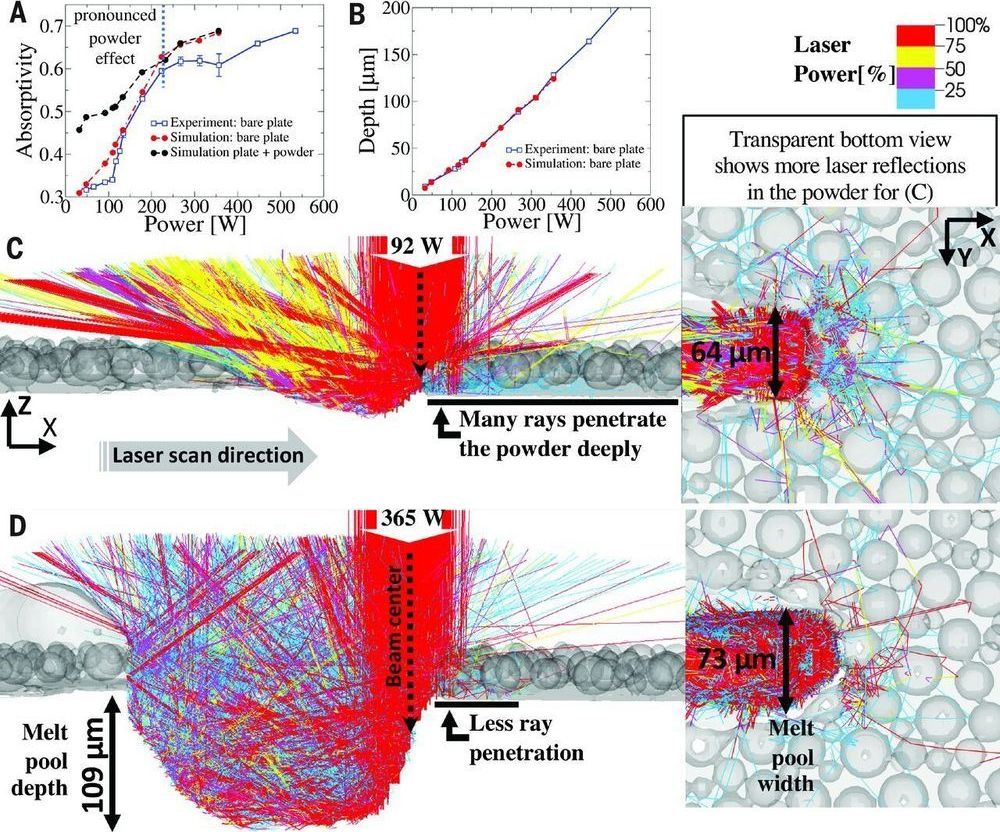
To better understand why the L-PBF process leads to so many defects (such as undesired pores) the researchers conducted X-ray synchrotron experiments and built predictive multi-physics models to gain a better understanding of what occurs during printing. One of their goals was to better understand how energy is absorbed during printing with powder layers that are only a few particles thick.








Comments are closed.