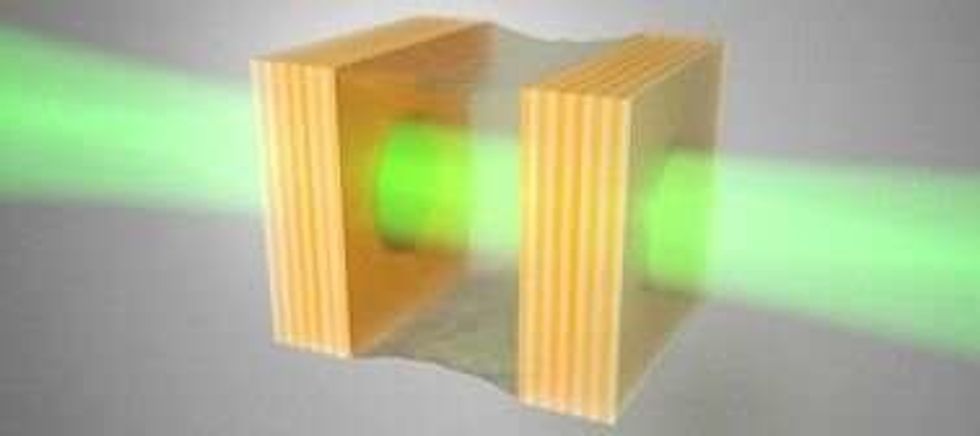
The research team, which also included Rodriguez’w PhD students Zou Geng and Kevin Peters, increased and decreased the distances between the mirrors at different speeds and noted how light transmitted through the cavity was affected. They saw that the direction in which the mirrors moved influenced how much light got through the cavity, finding that “the transmission of light through the cavity is non-linear.” This behavior of light, called hysteresis, is present in the phase transitions of boiling water or magnetic materials.
The scientists also increased the speed with which the oil-filled cavity opened and closed, observing that under such conditions the hysteresis was not always present. This allowed them to extrapolate a universal law. “The equations that describe how light behaves in our oil-filled cavity are similar to those describing collections of atoms, superconductors and even high energy physics,” elaborated Rodriguez, adding: “Therefore, the universal behavior we discovered is likely to be observed in such systems as well.”









Comments are closed.