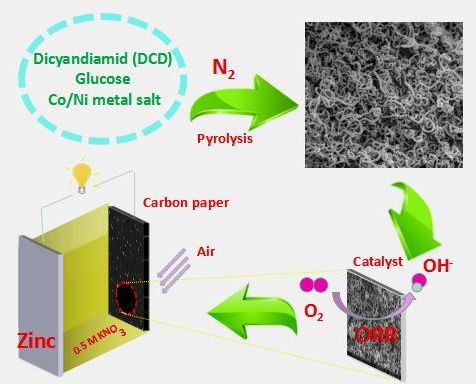
In a paper to be published in the forthcoming issue in NANO, a team of researchers from the School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering at Hunan University of Science and Technology have proposed a novel strategy for the synthesis of non-precious metal catalysts in zinc-air batteries that do not compromise its electroactivity, affordability and stability.
As a green and sustainable energy generator, zinc-air battery has attracted great attention from researchers due to its high specific energy, high current density, low cost, and environmental friendliness. Yet it is not without its drawbacks. The slow oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) of its cathode has become an obstacle to its commercial application. One possible solution is to use platinum (Pt) and Pt-based catalysts, but its high cost and scarce availability make it less ideal. In addition, alkaline KOH (or NaOH) is generally used as the electrolyte, but it leads to the generation of carbonates (CO32-) due to the dissolution of CO2 in the electrolyte as well as the spontaneous corrosion of the anodic zinc in strong alkaline media. This has the effect of slowing down the ionic conductivity of the electrolyte and battery life. Therefore, a neutral electrolyte should be used instead.








Comments are closed.