Nice.
Summary: Newly developed software allows researchers to study synaptic plasticity in dendritic spines.
Source: max planck florida institute for neuroscience.
Researchers at Max Planck Florida Institute for Neuroscience have developed new software to study synaptic plasticity in dendritic spines.
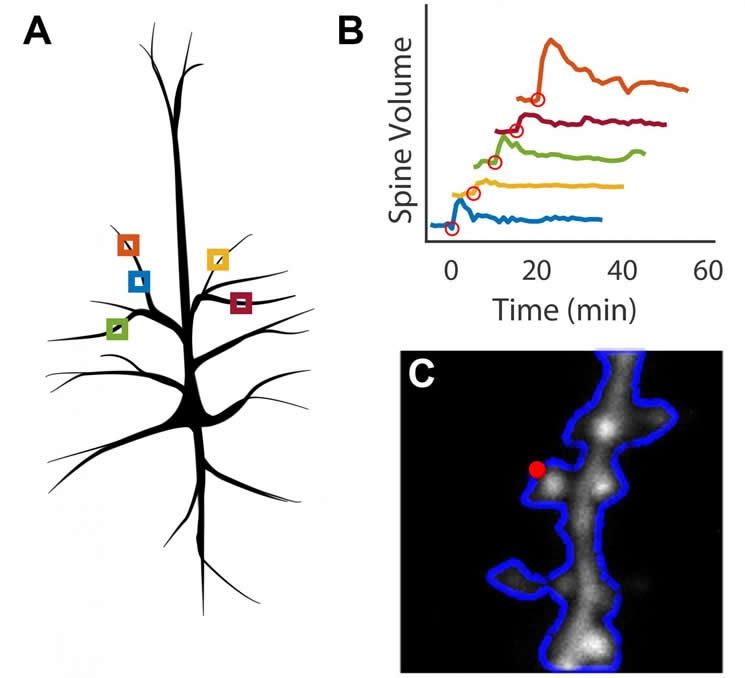
When humans and animals learn and form memories, the physical structures of their brain cells change. Specifically, small protrusions called dendritic spines, which receive signals from other neurons, can grow and change shape indefinitely in response to stimulation. Scientists at Max Planck Florida Institute for Neuroscience (MPFI) have observed this process, known as long-term structural plasticity, in individual spines, but doing so requires substantial time and effort. A new technique, developed by MPFI researchers, automates the process to make observing and quantifying this growth far more efficient. The open-source method is available to any scientist hoping to image plasticity as it happens in dendritic spines using Scanimage. The work was published in January 2016 in the Public Library of Science journal, PLOS ONE.








Comments are closed.