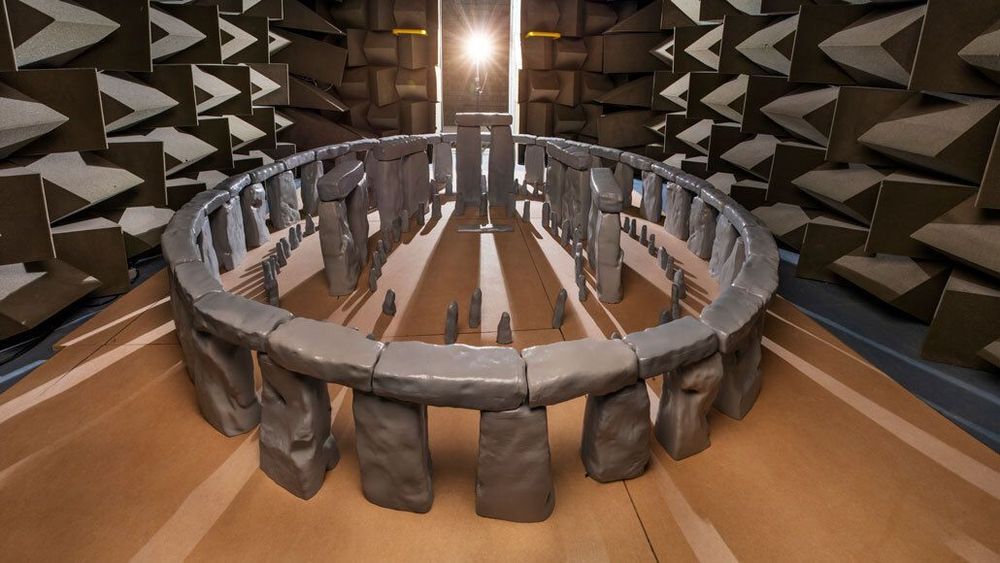
Scientists created a scale model one-twelfth the size of the ancient stone circle to study its acoustics.
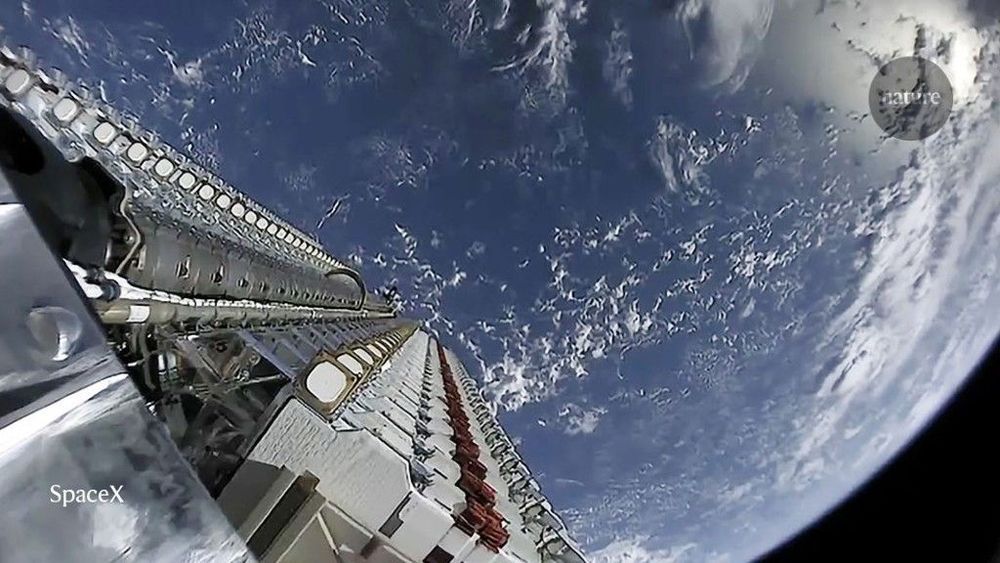



‘Megaconstellations’ of satellites increasingly launching into orbit around Earth will contaminate the data astronomers collect — and profoundly shift humanity’s view of the night skies. That’s the conclusion of the most detailed assessment yet of how these satellite networks, launched by companies including Amazon and SpaceX, might affect astronomical observations from Earth.
Most detailed report yet about the impact of giant satellite clusters says damage to observations is unavoidable — and offers mitigation strategies. Most detailed report yet about the impact of giant satellite clusters says damage to observations is unavoidable.

Straubel was an early founding member of Tesla and the company Chief Technology Officer until last summer.
He officially moved to an advisory role at the company, but it is believed to have been a symbolic move to soften the blow of Tesla’s longtime technology leader leaving the company.
As we reported at the time, Straubel was already becoming less present at Tesla months prior to the announcement and spending more time on his startup: Redwood Materials.


Enstatite chondrite meteorites, once considered ‘dry,’ contain enough water to fill the oceans — and then some.
A new study finds that Earth’s water may have come from materials that were present in the inner solar system at the time the planet formed — instead of far-reaching comets or asteroids delivering such water. The findings published on August 28, 2020, in Science suggest that Earth may have always been wet.
Researchers from the Centre de Recherches Petrographiques et Geochimiques (CRPG, CNRS/Universite de Lorraine) in Nancy, France, including one who is now a postdoctoral fellow at Washington University in St. Louis, determined that a type of meteorite called an enstatite chondrite contains sufficient hydrogen to deliver at least three times the amount of water contained in the Earth’s oceans, and probably much more.
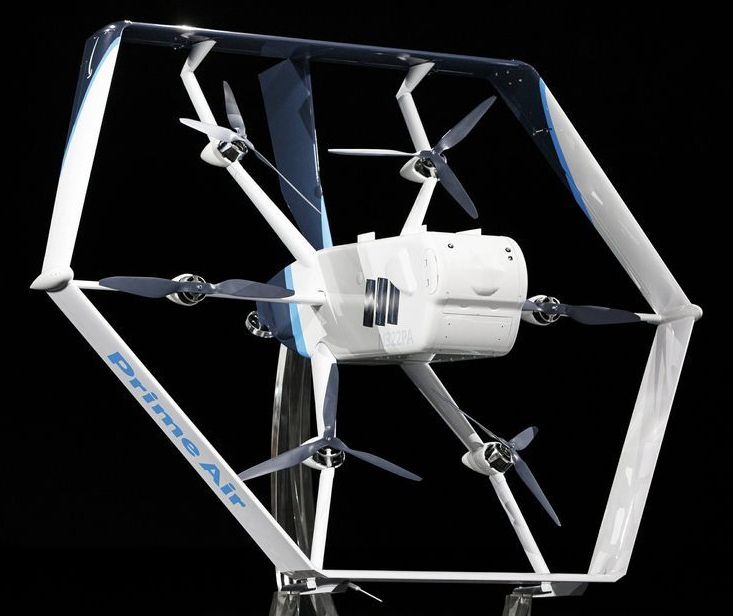

NEW YORK (AP) — Getting an Amazon package delivered from the sky is closer to becoming a reality.
The Federal Aviation Administration said Monday it had granted Amazon approval to deliver packages by drones.
Amazon said that the approval is an “important step,” but added that it is still testing and flying the drones. It did not say when it expected drones to make deliveries to shoppers.

A startup energy company in New Zealand believes it can power the world with a wireless electric transmission system that can bring power to hard-to-reach areas and do so at lower cost than with traditional power lines.
The startup, Emrod, has teamed up with a leading power supply company to test power transmission using a series of antennas. The only limiting factor is the antennas must be within line of sight with each other.
The system consists of a power source, a transmitting antenna, multiple relay stations, and a receiving antenna, often referred to as a “rectenna.”

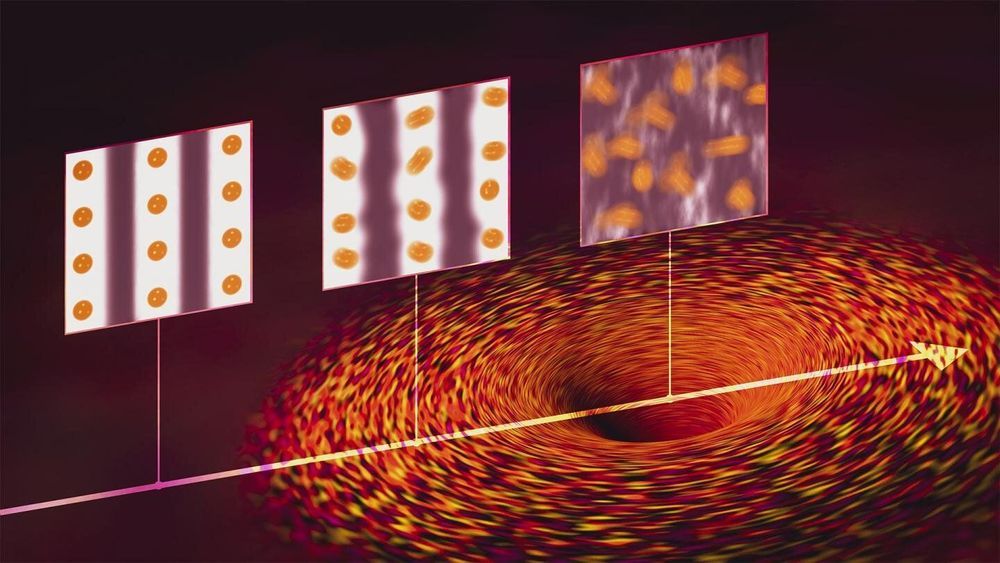
Among all the curious states of matter that can coexist in a quantum material, jostling for preeminence as temperature, electron density and other factors change, some scientists think a particularly weird juxtaposition exists at a single intersection of factors, called the quantum critical point or QCP.
“Quantum critical points are a very hot issue and interesting for many problems,” says Wei-Sheng Lee, a staff scientist at the Department of Energy’s SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory and investigator with the Stanford Institute for Materials and Energy Sciences (SIMES). “Some suggest that they’re even analogous to black holes in the sense that they are singularities—point-like intersections between different states of matter in a quantum material—where you can get all sorts of very strange electron behavior as you approach them.”
Lee and his collaborators reported in Nature Physics today that they have found strong evidence that QCPs and their associated fluctuations exist. They used a technique called resonant inelastic X-ray scattering (RIXS) to probe the electronic behavior of a copper oxide material, or cuprate, that conducts electricity with perfect efficiency at relatively high temperatures.