Hyperspectral imaging (HSI) is a state-of-the-art technique that captures and processes information across a given electromagnetic spectrum. Unlike traditional imaging techniques that capture light intensity at specific wavelengths, HSI collects a full spectrum at each pixel in an image. This rich spectral data enables the distinction between different materials and substances based on their unique spectral signatures.
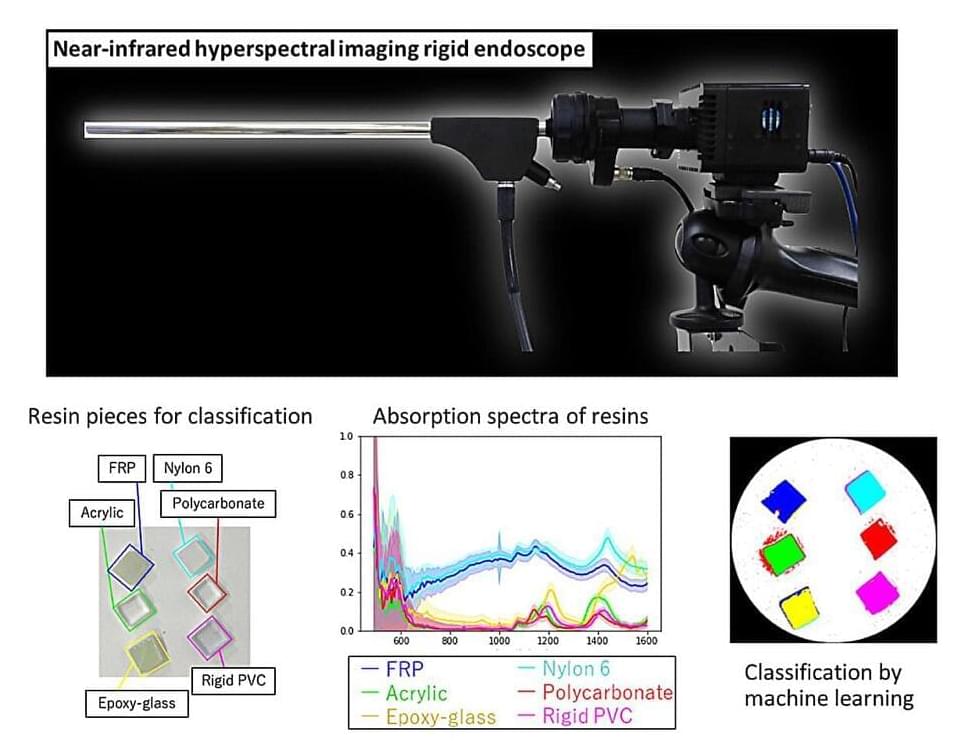
Near-infrared hyperspectral imaging (NIR-HSI) has attracted significant attention in the food and industrial fields as a non-destructive technique for analyzing the composition of objects. A notable aspect of NIR-HSI is over-thousand-nanometer (OTN) spectroscopy, which can be used for the identification of organic substances, their concentration estimation, and 2D map creation. Additionally, NIR-HSI can be used to acquire information deep into the body, making it useful for the visualization of lesions hidden in normal tissues.
Various types of HSI devices have been developed to suit different imaging targets and situations, such as for imaging under a microscope or portable imaging and imaging in confined spaces. However, for OTN wavelengths, ordinary visible cameras lose sensitivity and only a few commercially available lenses exist that can correct chromatic aberration. Moreover, it is necessary to construct cameras, optical systems, and illumination systems for portable NRI-HSI devices, but no device that can acquire NIR-HSI with a rigid scope, crucial for portability, has been reported yet.