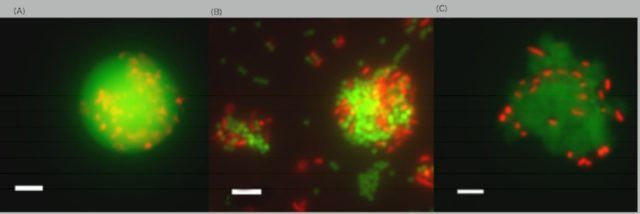
Researchers at Heriot-Watt University in Edinburgh used water collected from the Faroe-Shetland Channel and the Firth of Forth to set up their experiments. Plastics were added to the seawater and then incubated in conditions simulating the ocean’s surface. Within minutes, the minuscule pieces of plastic grouped together with bacteria, algae and other organic particles. The scientists are said to have been surprised to discover large masses of biopolymers formed the bulk of these plastic agglomerates. Team member Stephen Summers said: “This is a first step towards understanding how nanoplastics interact with natural biopolymers throughout the world’s oceans. ”This is very important, as it is at this small scale that much of the world’s biogeochemistry occurs. ”We found that the biopolymers envelope or engulf the nanoplastic particles, which caused the plastics to agglomerate into clumps. ”The nanoplastics, which are 100–200 times smaller than a bacterial cell, were actually incorporated into the agglomerates, which became visible to the naked eye in our lab experiments. ”The fact that these agglomerates become large enough to see raises concern, as they are likely to be seen as a food source by small marine animals.” We found that the biopolymers envelope or engulf the nanoplastic particles, which caused the plastics to agglomerate into clumps.
Researchers said micro and nano plastic particles mix with the bacteria secretions within minutes, forming clumps.

Continue reading “Plastics are being glued together in the ocean by bacteria, scientists find” »
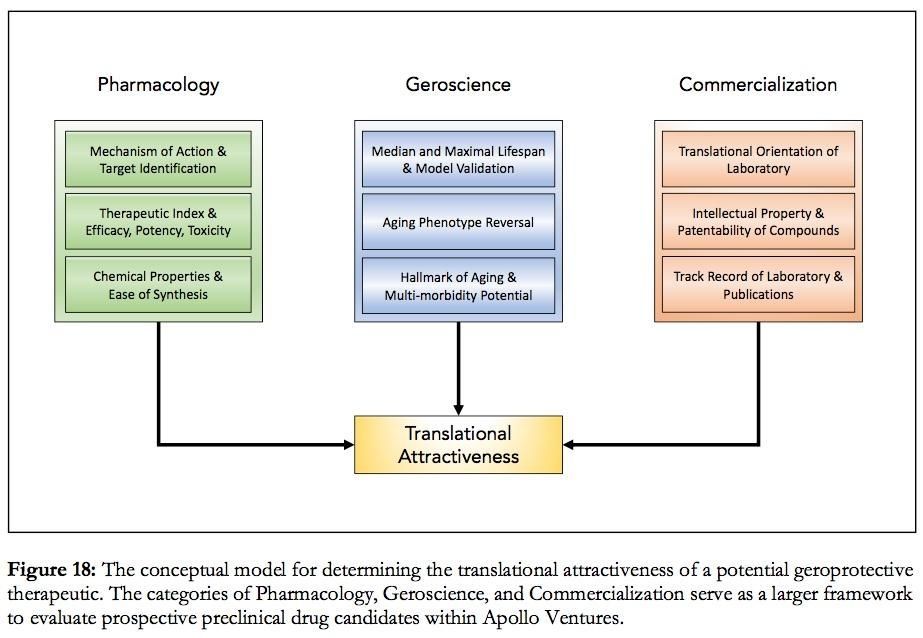
 Sebastian Aguiar is a Venture Fellow at Apollo Ventures, an aging-focused venture capital fund and company builder that invests across Europe and the United States. He can be found at https://www.linkedin.com/in/sebastianaguiar/ and https://twitter.com/sebastian_gero.
Sebastian Aguiar is a Venture Fellow at Apollo Ventures, an aging-focused venture capital fund and company builder that invests across Europe and the United States. He can be found at https://www.linkedin.com/in/sebastianaguiar/ and https://twitter.com/sebastian_gero.