Page 8810
May 22, 2019
How Did Life Arrive on Land? A Billion-Year-Old Fungus May Hold Clues
Posted by Genevieve Klien in category: futurism
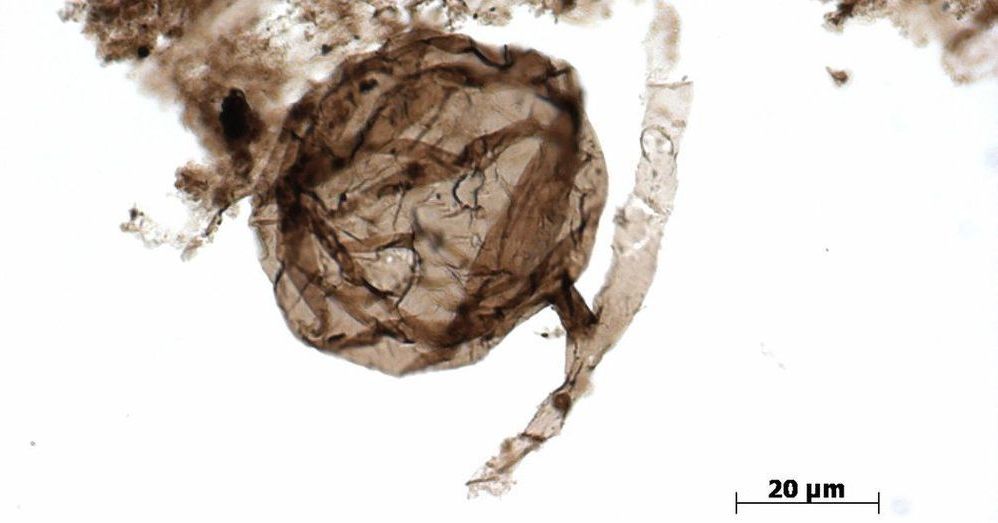
A cache of microscopic fossils from the Arctic hints that fungi reached land long before plants.
May 22, 2019
This is the world’s rarest form of gold. New clues are revealing why
Posted by Genevieve Klien in category: futurism
More than 130 years after its discovery, scientists just got their first high-tech peek at the unexpected crystal structure inside the Ram’s Horn.
May 22, 2019
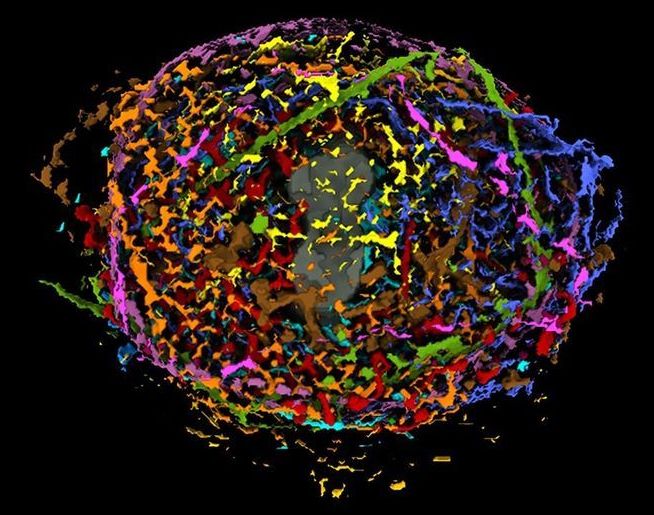
Computerized Model Reveals Details Of How Human Cells Divide
Posted by Genevieve Klien in category: biotech/medical
The nonprofit Allen Institute in Seattle has produced a visualization of human cell division that promises to be useful for professional scientists and curious amateurs alike.
May 22, 2019
Civil War plant medicines blast drug-resistant bacteria in lab tests
Posted by Quinn Sena in category: biotech/medical
During the height of the Civil War, the Confederate Surgeon General commissioned a guide to traditional plant remedies of the South, as battlefield physicians faced high rates of infections among the wounded and shortages of conventional medicines. A new study of three of the plants from this guide—the white oak, the tulip poplar and the devil’s walking stick—finds that they have antiseptic properties.
Scientific Reports is publishing the results of the study led by scientists at Emory University. The results show that extracts from the plants have antimicrobial activity against one or more of a trio of dangerous species of multi-drug-resistant bacteria associated with wound infections: Acinetobacter baumannii, Staphylococcus aureus and Klebsiella pneumoniae.
“Our findings suggest that the use of these topical therapies may have saved some limbs, and maybe even lives, during the Civil War,” says Cassandra Quave, senior author of the paper and assistant professor at Emory’s Center for the Study of Human Health and the School of Medicine’s Department of Dermatology.
Continue reading “Civil War plant medicines blast drug-resistant bacteria in lab tests” »
May 22, 2019
Cyber attacks are rewriting the ‘rules’ of modern warfare—and we aren’t prepared for the consequences
Posted by Quinn Sena in categories: cybercrime/malcode, government, military
Governments are becoming ever more reliant on digital technology, making them more vulnerable to cyber attacks. In 2007, Estonia was attacked by pro-Russian hackers who crippled government servers, causing havoc. Cyber attacks in Ukraine targeted the country’s electricity grid, while Iran’s nuclear power plants were infected by malware that could have led to a nuclear meltdown.
In the US, president Trump recently declared a “national emergency” to recognise the threat to US computer networks from “foreign adversaries”.
Politically-motivated cyber attacks are becoming increasingly commonplace but unlike traditional warfare between two or more states, cyberwarfare can be launched by groups of individuals. On occasion, the state is actually caught in the crosshairs of competing hacking groups.
May 22, 2019
Physicists propose a second level of quantization for quantum Shannon theory
Posted by Quinn Sena in category: quantum physics
Information theory, which was developed by Claude Shannon starting in the late 1940s, deals with questions such as how quickly information can be sent over a noisy communications channel. Both the information carriers (e.g., photons) and the channel (e.g., optical fiber cable) are assumed to be clas…
May 22, 2019
Why Cryonics Makes Sense
Posted by Paul Battista in categories: cryonics, life extension
The more I read about cryonics—i.e. freezing yourself after death—the more I realized it’s something we should all be talking about.
May 22, 2019
Successful Life Extension Study Is a Sign That Aging Can Be Stalled
Posted by Paul Battista in categories: biotech/medical, life extension
May 22, 2019
Senescent Cells and Cataract Development
Posted by Paul Battista in category: life extension
In a recent study, researchers have explored senescence-related proteins and protein interactions in cataracts, a leading cause of visual impairment and blindness in older adults.
Cataracts are characterized by the clouding of the lens in the eye, which leads to impaired vision. Cataracts generally develop slowly and can affect either one or both eyes at the same time. Cataract symptoms typically include faded colors, blurry or double vision, halos around light, trouble with bright lights, and difficulty seeing at night.
By analyzing proteins and their interactions, these researchers aim for a full understanding of this condition, showing that multiple biomarkers associated with aging rise during the formation of cataracts. Typically, p53, a well-known biomarker for the presence of senescent cells, is seen to rise along with transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-β1), another biomarker commonly associated with inflammation when encountered in high amounts. During the development of cataracts, the number of senescent cells rises, as this research shows.
Continue reading “Senescent Cells and Cataract Development” »