Page 8794
May 28, 2019
Stay on top ofthe latestengineering news
Posted by Klaus Baldauf in categories: engineering, robotics/AI
Top artificial intelligence (AI) expert and founder and CEO of Fountech.ai Nikolas Kairinos said in a Daily Star interview that within 20 years we could have implants put into our heads that will allow us to learn everything. “You won’t need to memorize anything,” said the specialist to the Daily Star.
RELATED: NEURALINK: HOW THE HUMAN BRAIN WILL DOWNLOAD DIRECTLY FROM A COMPUTER
May 27, 2019
Autism linked to ‘junk’ DNA mutations
Posted by Xavier Rosseel in categories: biotech/medical, neuroscience
Mutations in so-called “junk” DNA have been tied to the development of autism (ASD) in children who do not have parents or siblings with the condition.
For the first time, research links non-coding DNA to disorder development. Andrew Masterson reports.
May 27, 2019
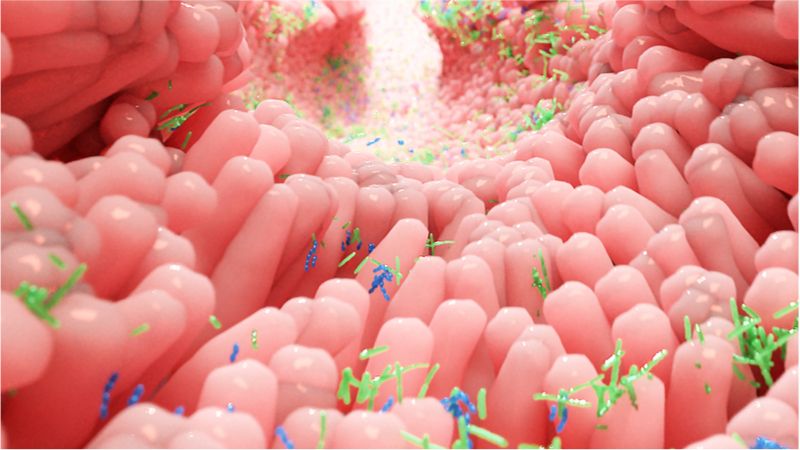
Signs of selection in the stomach
Posted by Xavier Rosseel in categories: biotech/medical, evolution, genetics
Helicobacter pylori, a globally distributed gastric bacterium, is genetically highly adaptable. Microbiologists at LMU have now characterized its population structure in individual patients, demonstrating an important role of antibiotics for its within-patient evolution.
The cosmopolitan bacterium Helicobacter pylori is responsible for one of the most prevalent chronic infections found in humans. Although the infection often provokes no definable symptoms, it can result in a range of gastrointestinal tract pathologies, ranging from inflammation of the lining of the stomach to gastric and duodenal tumors. Approximately 1 percent of all those infected eventually develop stomach cancer, and the World Health Organization has classified H. pylori as a carcinogen. One of Helicobacter pylori’s most striking traits is its genetic diversity and adaptability. Researchers led by microbiologist Sebastian Suerbaum (Chair of Medical Microbiology and Hospital Epidemiology at LMU’s Max von Pettenkofer Institute have now examined the genetic diversity of the species in the stomachs of 16 patients, and identified specific adaptations that enable the bacterium to colonize particular regions of the stomach.
May 27, 2019
Artificial intelligence detects a new class of mutations behind autism
Posted by Paul Gonçalves in categories: biotech/medical, genetics, robotics/AI
Many mutations in DNA that contribute to disease are not in actual genes but instead lie in the 99% of the genome once considered “junk.” Even though scientists have recently come to understand that these vast stretches of DNA do in fact play critical roles, deciphering these effects on a wide scale has been impossible until now.
Using artificial intelligence, a Princeton University-led team has decoded the functional impact of such mutations in people with autism. The researchers believe this powerful method is generally applicable to discovering such genetic contributions to any disease.
Publishing May 27 in the journal Nature Genetics, the researchers analyzed the genomes of 1,790 families in which one child has autism spectrum disorder but other members do not. The method sorted among 120,000 mutations to find those that affect the behavior of genes in people with autism. Although the results do not reveal exact causes of cases of autism, they reveal thousands of possible contributors for researchers to study.
Continue reading “Artificial intelligence detects a new class of mutations behind autism” »
May 27, 2019
Nutrient-Rich Diets May Lead to Dysbiosis and Age-Related Diseases
Posted by Steve Hill in categories: biotech/medical, life extension
The role that the gut microbiome plays in aging is increasingly being appreciated in the research world as more evidence arrives to support it. A new publication reviews the various supporting evidence and takes a look at the gut microbiome in the context of nutrient-rich diets and how they facilitate the progression of dysbiosis and disease [1].
What is the microbiome?
The microbiome is the varied community of bacteria, archaea, eukarya, and viruses that inhabit our guts. The four bacterial phyla of Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, Proteobacteria, and Actinobacteria comprise 98% of the intestinal microbiome.
Continue reading “Nutrient-Rich Diets May Lead to Dysbiosis and Age-Related Diseases” »
May 27, 2019
Raspberry-picking MACHINES will replace dwindling numbers of migrant farm workers
Posted by Carse Peel in categories: food, robotics/AI, sustainability

Hours spent toiling away under the beating sun to harvest berries and fruit may soon be a thing of the past as robots look set to replace humans in the field.
A £700,000 machine built by the University of Plymouth has succeeded in plucking a raspberry from a plant and carefully placing it in a punnet.
May 27, 2019
Luba Greenwood, J.D., Head of Strategic Business Development and Corporate Ventures at Verily (formerly Google Life Sciences) — ideaXme show — Ira Pastor
Posted by Ira S. Pastor in categories: aging, big data, bioengineering, business, finance, health, innovation, life extension, science, transhumanism

May 27, 2019
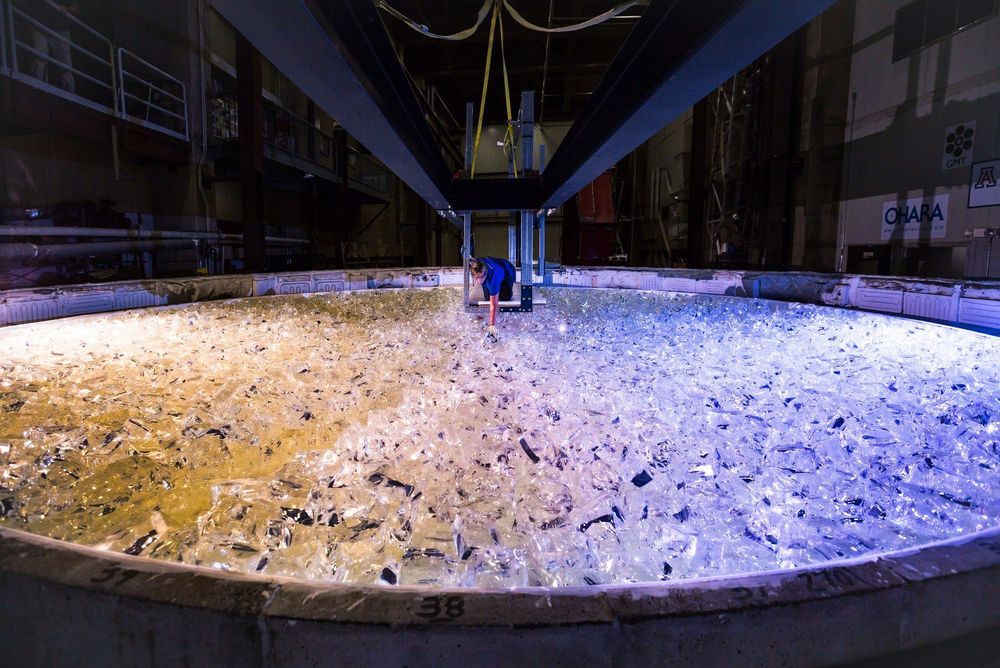
The Astounding Engineering Behind the Giant Magellan Telescope
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: education, engineering, habitats, space
It’s easy to miss the mirror forge at the University of Arizona. While sizable, the Richard F. Caris Mirror Laboratory sits in the shadow of the university’s much larger 56,000-seat football stadium. Even its most distinctive feature—an octagonal concrete prominence emblazoned with the school’s logo—looks like an architectural feature for the arena next door. But it’s that tower that houses some of the facility’s most critical equipment.
Inside the lab, a narrow, fluorescent-green staircase spirals up five floors to the tower’s entrance. I’m a few steps from the top when lab manager Stuart Weinberger asks, for the third time, whether I have removed everything from my pockets.
“Glasses, keys, pens. Anything that could fall and damage the mirror,” he says. Weinberger has agreed to escort me to the top of the tower and onto a catwalk some 80 feet above a mirror 27.5 feet in diameter. A mirror that has already taken nearly six years—and $20 million—to make. “Most people in the lab aren’t even allowed up here,” he says. That explains Weinberger’s nervousness about the contents of my pockets (which are really, truly empty), and why he has tethered my camera to my wrist with a short line of paracord.
Continue reading “The Astounding Engineering Behind the Giant Magellan Telescope” »
May 27, 2019
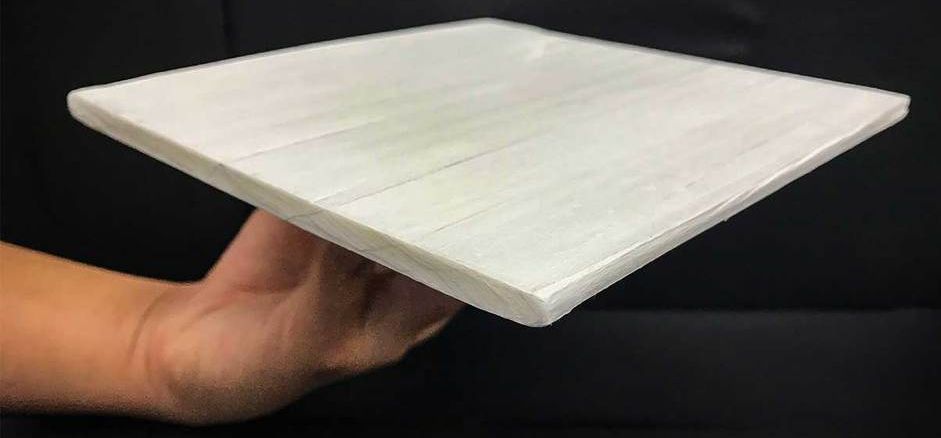
Researchers develop wood that can cool a home
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: habitats, materials
Wood has a series of tiny structures inside that are used to carry water and nutrients to all parts of a living tree. Scientists have now figured out how to harness those same small structures to keep a home cool. Researchers at the University of Maryland and the University of Colorado Boulder say that the material could save 20% in AC bills.