Page 770
Apr 8, 2024
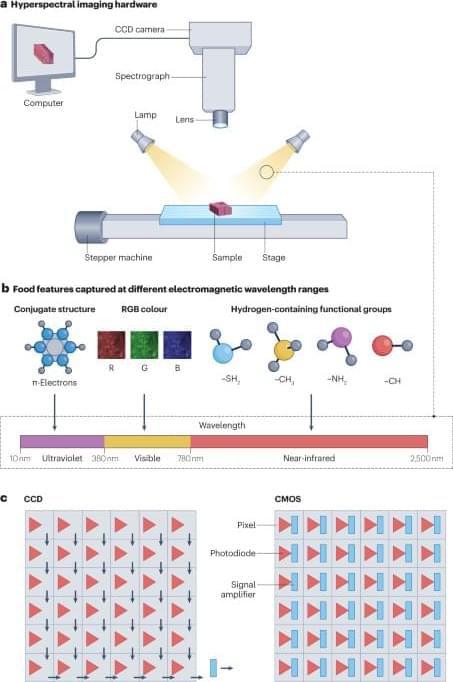
Applications of hyperspectral imaging technology in the food industry
Posted by Shubham Ghosh Roy in category: food
Rational and scientific use of hyperspectral imaging involves the selection of appropriate imaging hardware and data analysis software. Sun et al. describe applications of hyperspectral imaging in food quality inspection and provide guidance for non-specialist researchers aiming to implement this technology.
Apr 8, 2024
AI solves Schrödinger’s Equation
Posted by Shubham Ghosh Roy in categories: chemistry, information science, particle physics, quantum physics, robotics/AI, space
A newly developed AI method can calculate a fundamental problem in quantum chemistry: Schrödinger’s Equation. The technique could calculate the ground state of the Schrödinger equation in quantum chemistry.
Predicting molecules’ chemical and physical properties by relying on their atoms’ arrangement in space is the main goal of quantum chemistry. This can be achieved by solving the Schrödinger equation, but in practice, this is extremely difficult.
Apr 7, 2024
New research traces the fates of stars living near the Milky Way’s central black hole
Posted by Shubham Ghosh Roy in category: cosmology
Despite their ancient ages, some stars orbiting the Milky Way’s central supermassive black hole appear deceptively youthful. But unlike humans, who might appear rejuvenated from a fresh round of collagen injections, these stars look young for a much darker reason.
Apr 7, 2024
Worrying research show the Earth’s rotation is beginning to change
Posted by Shubham Ghosh Roy in categories: climatology, sustainability
Link :
Experts are concerned about the way our planet is rotating due to climate change. For years, scientists have been concerned about the impacts of global warming.
Now, new research has revealed a change in the Earth’s spin due to the melting of the ice poles.
Continue reading “Worrying research show the Earth’s rotation is beginning to change” »
Apr 7, 2024
Largest 3D map of our universe could hint that dark energy evolves with time
Posted by Shubham Ghosh Roy in category: cosmology
Apr 7, 2024
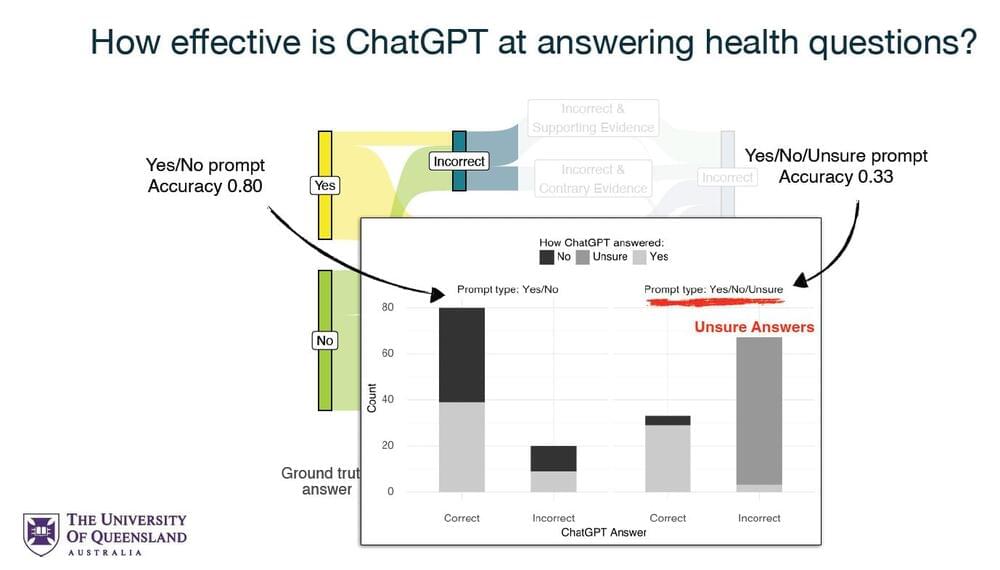
Study reveals the impact of prompt design on ChatGPT’s health advice accuracy
Posted by Shubham Ghosh Roy in categories: health, robotics/AI
Study: Dr ChatGPT tell me what I want to hear: How different prompts impact health answer correctness
As AI becomes increasingly integral to our daily lives, its ability to provide accurate and reliable information, particularly in sensitive areas such as health, is under intense scrutiny. The study conducted by CSIRO and The University of Queensland researchers brings to light the nuanced ways in which the formulation of prompts influences ChatGPT’s responses. In the realm of health information seeking, where the accuracy of the information can have profound implications, the findings of this study are especially pertinent.
Using the Text Retrieval Conference (TREC) Misinformation dataset, the study precisely evaluated ChatGPT’s performance across different prompting conditions. This analysis revealed that ChatGPT could deliver highly accurate health advice, with an effectiveness rate of 80% when provided with questions alone. However, this effectiveness is significantly compromised by biases introduced through the phrasing of questions and the inclusion of additional information in the prompts.
Apr 7, 2024
Wound warriors: How microbes influence healing and infection risks
Posted by Shubham Ghosh Roy in category: biotech/medical
🦠🔬🩹
Study explores how wound microbiota affect skin repair and infection risk by altering host immune responses, underscoring the complexity of microbial interactions in wound healing.
Apr 7, 2024
To stay safe in Windows 10 from next October commercial customers have to pay $61, then ‘double every consecutive year for a maximum of three years’
Posted by Genevieve Klien in category: security
Commercial customers will have to get their wallets ready to keep receiving security updates for Windows 10.
Apr 7, 2024
New window film drops temperature, slashes energy consumption
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: quantum physics, robotics/AI
Assisted by quantum physics and machine learning, researchers have developed a transparent window coating that lets in visible light but blocks heat-producing UV and infrared. The coating not only reduces room temperature but also the energy consumption related to cooling, regardless of where the sun is in the sky.
Windows are great. They provide views of the park you live across from or the bird-filled tree outside your office. But, windows can also be not-so-great. Letting in light (and the view) is one thing, but with light comes heat, especially in the hotter months.
On hot days, up to 87% of heat gain in our homes is through windows. UV radiation from sunlight passes easily through glass, heating up the room and increasing the likelihood that you need to turn on the air-con or else forgo any light (and, again, that view) by closing the curtains or lowering the blinds. However, researchers at the University of Notre Dame have developed a window coating that blocks heat-producing UV and infrared light while allowing visible light in, reducing both room temperature and cooling energy consumption.